Beyond their views of the personal impact of various technologies, publics in these countries are divided over how the internet in general has impacted politics in their societies. An 11-country median of 44% say the increasing use of the internet has had a good impact on politics, but 28% feel that impact has been largely bad – and this balance of opinion is most negative in Tunisia, Jordan and Lebanon.
Adults in these countries also feel access to technology has had a variety of both positive and negative impacts on their fellow citizens. On the positive side of the ledger, a median of 78% say access to the internet, mobile phones and social media has made people more informed about current events. And when asked about the impact of social media on the broader political process, majorities in nine of these 11 countries say they have increased the ability for ordinary citizens to take part in the political process.
At the same time, an 11-country median of 72% say these technologies have made people easier to manipulate with rumors and false information. And majorities in eight countries say social media have increased the risk that citizens might be manipulated by domestic politicians.
Mixed attitudes about the internet’s overall impact on politics
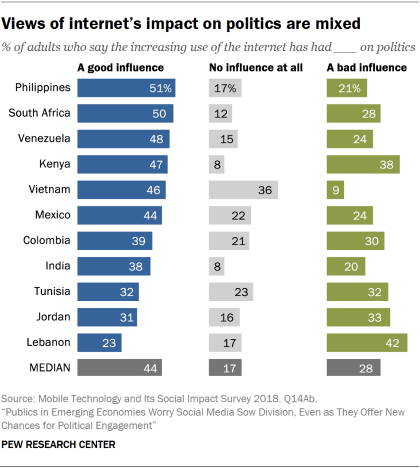
Adults in these countries express mixed views about the overall influence of the internet on politics. In most countries, larger shares say the internet has had a good impact on politics than say the same about issues such as children or morality. But notably smaller shares say the internet has had a good impact on politics than say this about its effect on issues such as education, the economy or local culture (for more, see the first report in this series).
Adults in these countries also make little distinction between the impact of the internet and mobile phones when it comes to politics. Nearly identical shares say the internet and mobile phones have had a good, bad or negligible impact on politics.
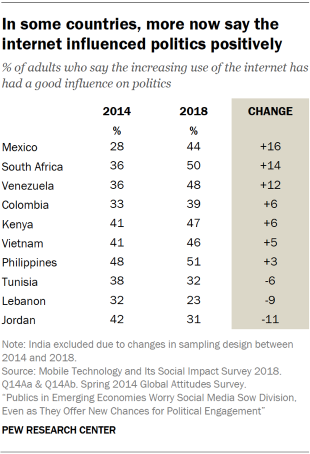
Across these 11 countries, public opinion about the internet’s impact on politics is most negative in Jordan, Lebanon and Tunisia. In Lebanon, nearly twice as many say the internet has had a bad (42%) rather than good (23%) influence on politics. And in Jordan and Tunisia, the shares saying the internet’s impact on politics has been good are comparable to the shares saying it has been bad.
In addition to having a comparably negative balance of sentiment relative to the other countries in this survey, publics in these three countries have also turned somewhat less upbeat in recent years in their assessments of the internet’s impact on politics. From 2014 to 2018, the share of adults in these countries saying the internet has had a good influence on politics has declined by 11 percentage points in Jordan, 9 points in Lebanon and 6 points in Tunisia. By contrast, sentiment in the other seven countries for which trends are available either grew more positive or stayed largely the same over that time. This positive shift has been most pronounced in Mexico, South Africa and Venezuela.
Many think technology has made people better informed – but also easier to manipulate
When asked about the impact of mobile phones, the internet and social media on various political behaviors and attitudes, people in these nations tend to express seemingly dual views of how technology has brought “more” to society: that it has made people more informed, yet more manipulatable; more divided, yet sometimes more accepting of others.
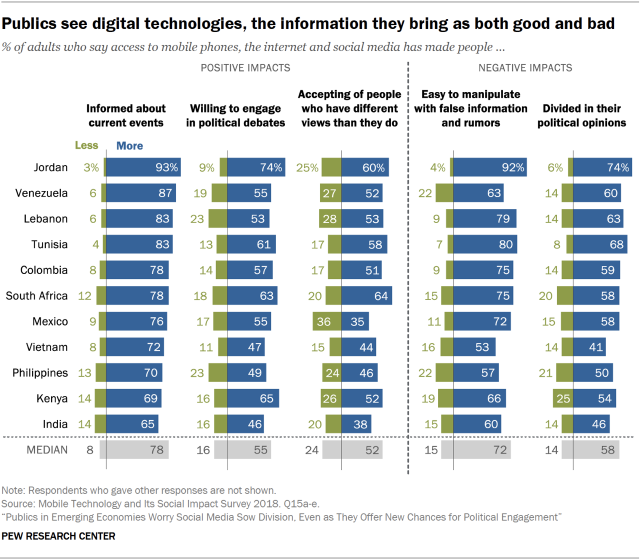
At one level, publics in these countries believe that technology simultaneously makes people more informed and more gullible. Majorities in every country – and an 11-country median of 78% – say access to technology has made people more informed about current events. At the same time, majorities in every country except for Vietnam – and an 11-country median of 72% – say technology has made it easier to manipulate people with false information and rumors.
We become numb to the news, like the presidential campaigns in Mexico. A term ago, we were struggling to get more political awareness, and now everything is made a meme and laughed at. It defeats the purpose of the internet.MAN, 28, MEXICO
MAN, 28, MEXICO
The survey highlights similar tensions over whether these technologies make people more divided or more accepting of others. A median of 58% say access to mobile phones, the internet and social media has made people more divided in their political opinions. At the same time, a median of 52% say these technologies have made people more accepting of those who have different views than they do. And a median of 55% say they have generally made people more willing to engage in political debates.
These positive and negative views of technology’s impact on political attitudes are often related. In 10 of the 11 countries surveyed, those who believe technology has made people more informed are more likely than others to say technology has also made people easier to manipulate.
Similarly, in most countries those who say technology has made people more accepting of diverse viewpoints are simultaneously more likely to say it has made people more divided in their political opinions.
Through our mobile phones, since there is that social media, it has really led to the spread of hatred and tribalism amongst ourselves.MAN, 38, KENYA
MAN, 38, KENYA
These same costs and benefits are visible when it comes to technology’s impact on political news and discussion. For instance, people in these countries overwhelmingly feel mobile phones have improved people’s ability to obtain news. Yet an 11-country median of 64% say people should be very concerned about exposure to false information when using their mobile devices.
People in some countries stand out for their views on the influence of technology on politics
Especially large shares of Jordanians feel technology has made people more receptive to most of the political impacts measured in the survey, and this is especially true of the notion that technology makes people more informed but also easier to manipulate. Around nine-in-ten Jordanians say access to mobile phones, the internet and social media has made people more informed about current events, but a similar share says this access makes them more vulnerable to being manipulated with rumors and false information. And roughly three-quarters of Jordanians say technology has made people more divided in their political opinions, but also more willing to engage in political debates.
By contrast, Vietnamese adults are relatively likely to say access to these technologies hasn’t changed much compared with those in the other countries surveyed. One-third or more Vietnamese say these technologies haven’t had much impact on people’s willingness to engage in political debates (33%), how divided they are in their political opinions (35%) or how accepting they are of those with different views (35%), while 26% say they haven’t had much impact on how easy people are to manipulate. In each instance, these represent the largest shares among the 11 countries surveyed.
Meanwhile, Mexicans stand out for their assessment of the impact of technologies on people’s tolerance of different viewpoints. Some 35% of Mexicans say technology has made people more accepting of people who have different views than they do, but a nearly identical share (36%) says technology has had a negative impact in this regard. Younger Mexicans are especially likely to say technologies have made people less tolerant to people who hold different views: 41% hold this view, compared with 30% of Mexicans ages 50 and older.
Social media users, those affiliated with a political party and the more educated are more likely to see both positive and negative political impacts of digital technologies
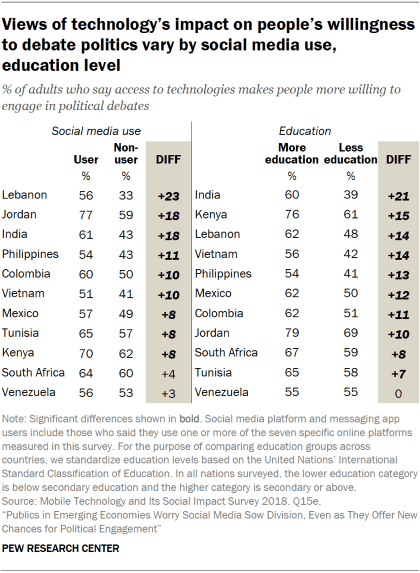
Certain groups are especially likely to cite both the positive and negative impacts of technology on political engagement.
For example, social media users are more likely than non-users to say technology has made people more informed about current events in all 11 countries surveyed; more accepting of people with different views in eight countries; and more willing to engage in political debates in nine countries.10 At the same time, in nine countries a larger share of users say technology is making people more divided in their political opinions – and in 10 countries a larger share of social media users say technology is making people easier to mislead with misinformation (see Appendix C for detailed tables).
These attitudes also vary by education level.11 Across all 11 countries, adults with a secondary education or higher are more likely to say technology has made people more informed about current events relative to those who do not have a secondary education. And in nine countries, adults with higher levels of educational attainment are more inclined to say technology has made people more subject to false information and rumors.
Meanwhile, adults with higher levels of educational attainment are more likely to say technology has contributed to both political divisions and tolerance of opposing viewpoints in seven of these countries (Colombia, India, Kenya, Lebanon, the Philippines, Tunisia and Vietnam).
In eight of the nine countries for which partisan information is available, those who have a partisan affiliation are somewhat more likely than those who don’t identify with any particular party to say technology has made people more willing to engage in political debate.12 And in five of those countries, those with a partisan affiliation are more likely to say access to technology has made people more divided in their political opinions. But in most countries, similar shares of the affiliated and unaffiliated say technology has made people more informed, more accepting of those with different viewpoints and more susceptible to misinformation.13
Lastly, social media users’ assessments of the impact of technology on political attitudes are somewhat related to whether they view social media as an important news source. In seven out of the 11 countries, those who say social media are a very important news source for them to get political news and information are more likely than users who do not think social media are as important to say technology has made people more informed about news and current events.
Social media seen to confer benefits – but also risks – on the overall political process
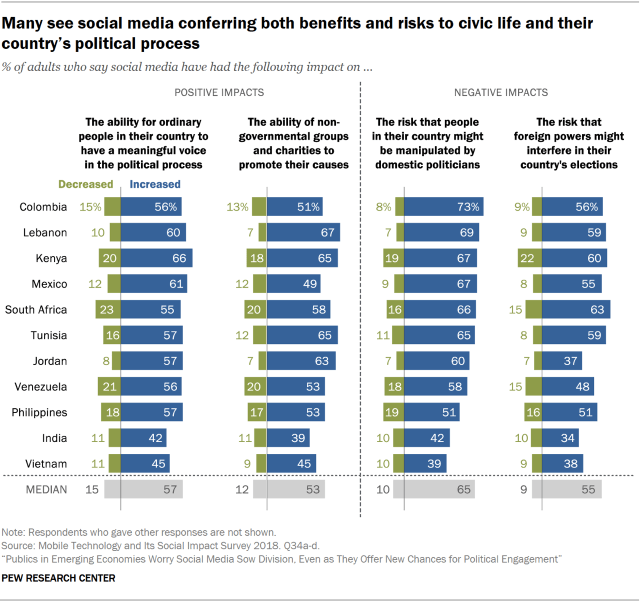
When asked about different impacts social media have had on their country’s political process, publics in these countries are more likely than not to say social media offer new avenues for political engagement. A median of 57% – and majorities in every country except for Vietnam and India – say social media have increased the ability for ordinary people in their country to have a meaningful voice in the political process. And a median of 53% say these platforms have increased the ability of nongovernmental organizations to promote their causes.
But these perceived benefits from social media are matched with perceived costs. An 11-country median of 65% say social media have increased the risk that people in their country might be manipulated by domestic politicians. And when asked whether these platforms might facilitate foreign interference in their country’s elections, a median of 55% say these platforms have indeed increased this risk – although a median of 27% feel they have not had much effect either way.
Now it is much easier for our countrymen to know about the plans of our government for our OFW [Overseas Filipino Workers].WOMAN, 48, PHILIPPINES
WOMAN, 48, PHILIPPINES
Among those who use social media, there are only minimal differences between the views of younger (ages 18 to 29) and older adults (those ages 50+) on these questions. However, there are some differences based on how extensively people rely on these platforms for information. In most countries, those who say social media are a very important news source are more likely to say these platforms have increased ordinary people’s ability to have a meaningful voice in politics, and that they have helped nongovernmental groups to promote their causes. At the same time, in seven countries this group is also more likely to say these platforms have increased the risk of people being manipulated by domestic politicians, compared with users who do not see social media as a very important source of information.
In several countries, sizable shares say they do not know how these platforms have impacted the broader political system
These questions were asked of all adults – regardless of whether they themselves use social media platforms or not. And in several of these countries, sizable shares of those who do not use any social media platforms are unable to offer an opinion on how social media have impacted these aspects of the political process. This is especially true in Jordan, Lebanon, India and Vietnam. Among people in these countries who do not use social media, as many as 21% of Vietnamese, 34% of Jordanians, 41% of Lebanese and 51% of Indians either do not know the answer to these individual questions or refused to offer a guess.
Similarly, demographic groups who use social media at low rates (such as older adults or those with lower levels of education) are often more likely to say they do not know how social media have impacted these elements of the political process.




