Online privacy is complex, encompassing debates over law enforcement’s data access, government regulation and what information companies can collect. This chapter examines Americans’ perspectives on these issues and highlights how views vary across different groups, particularly by education and age.
When managing their privacy online, most Americans say they trust themselves to make the right decisions about their personal information (78%), and a majority are skeptical that anything they do will make a difference (61%).
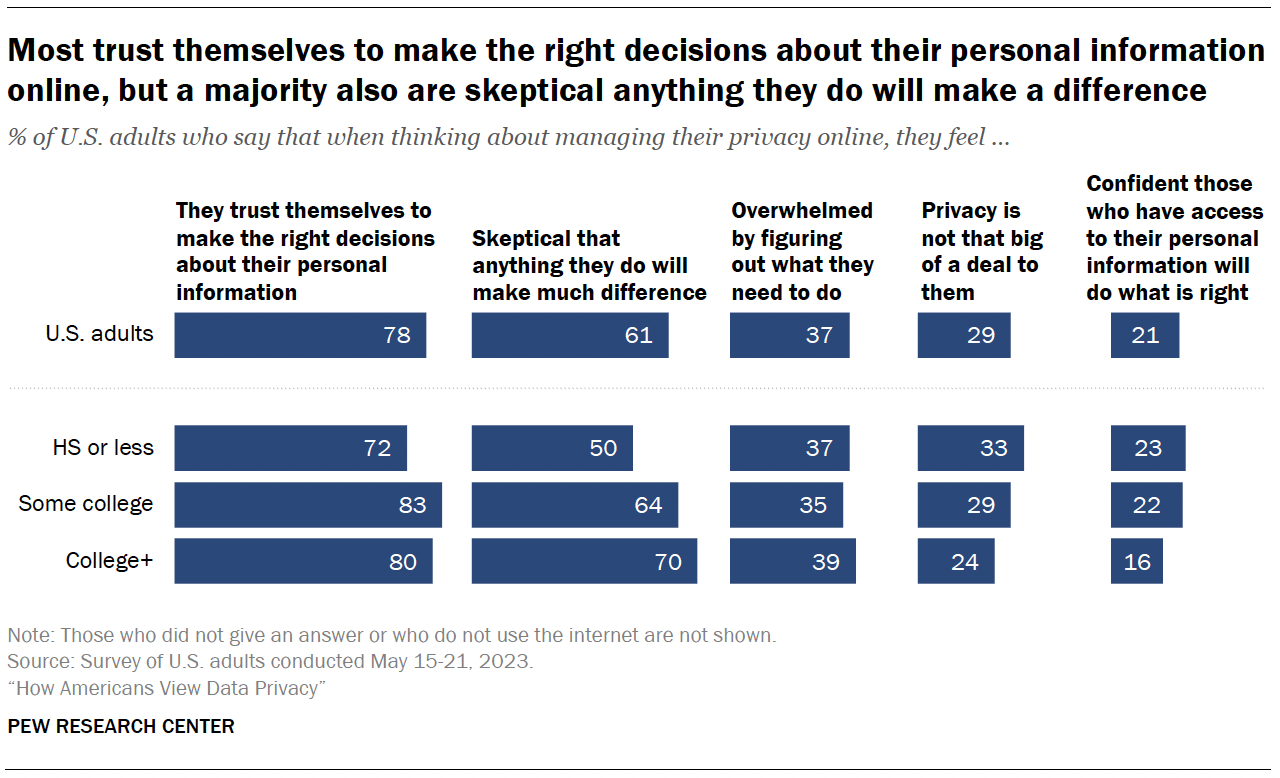
Far fewer mention being overwhelmed by figuring out what they need to do (37%) or say privacy is not that big of a deal to them (29%).
Another 21% are confident that those with access to their personal information will do what is right.
Education differences
- 81% of those with at least some college experience say they trust themselves to make the right decisions about their personal information online, compared with 72% of those with a high school diploma or less.
- 67% of those with at least some college are skeptical that anything they do to manage their online privacy will make a difference, compared with half of those with a high school diploma or less formal education.
On the other hand, those with a high school education or less are more likely than those with some college experience or more to say that privacy isn’t that big of a deal to them and that they are confident that those who have access to their personal information will do the right thing.
Personal data and information
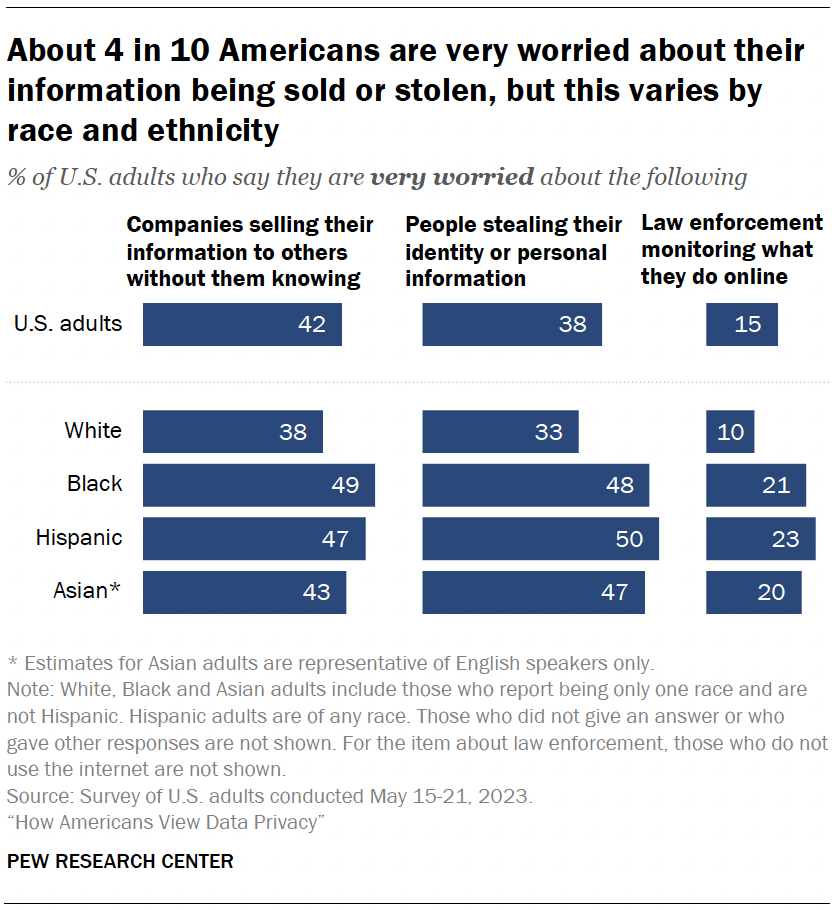
The survey also explores the concerns people have about data collection and security – specifically, how they feel about three scenarios around companies, law enforcement and identity theft.
Roughly four-in-ten Americans say they are very worried about companies selling their information to others without them knowing (42%) or people stealing their identity or personal information (38%). Fewer are apprehensive about law enforcement monitoring what they do online (15%).
Racial and ethnic differences
However, some of these shares are higher among Hispanic, Black or Asian adults:1
- Roughly half of Hispanic, Black or Asian adults are very worried about people stealing their identity or personal information, compared with a third of White adults.
- About one-in-five of each group are very worried about law enforcement monitoring their online activity; 10% of White adults say this.
Feelings of concern, confusion and a lack of control over one’s data
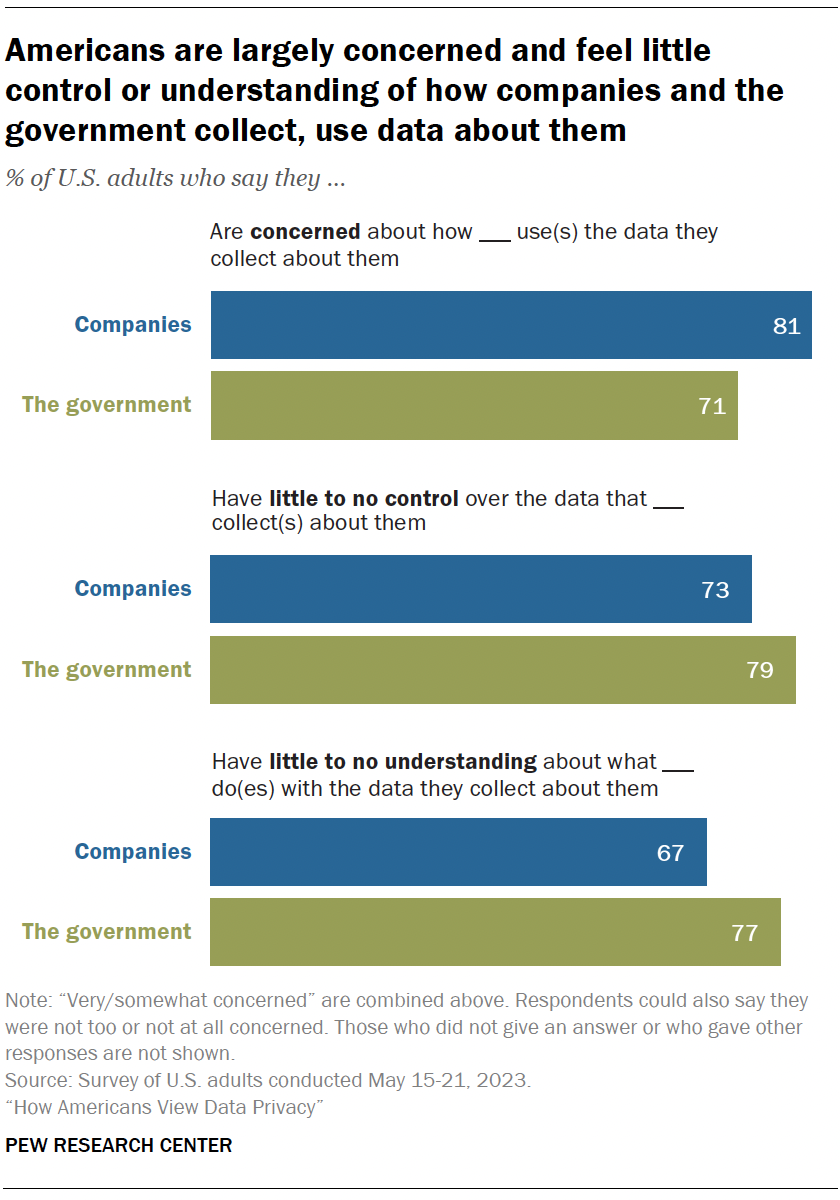
A majority of Americans say they are concerned, lack control and have a limited understanding about how the data collected about them is used. This is true whether it’s the government or companies using their data. Similar sentiments were expressed in 2019, when we last asked about this.
Concern is high: 81% say they feel very or somewhat concerned with how companies use the data they collect about them. Fully 71% say the same regarding the government’s use of data.
People don’t feel in control: Roughly three-quarters or more feel they have very little or no control over the data collected about them by companies (73%) or the government (79%).
Understanding is low: Americans also say they don’t understand what these actors are doing with the data collected about them. Majorities say they have very little or no understanding of this, whether by the government (77%) or companies (67%).
Americans are now less knowledgeable than before about how companies are using their personal data. The share who say they don’t understand this has risen from 59% in 2019 to 67% in 2023.
They have also grown more concerned about how the government uses the data it collects about them, with the share expressing concern up from 64% to 71% over this same period.
While these sentiments have not changed significantly since 2019 among Democrats and those who lean toward the Democratic Party, Republicans and GOP leaners have grown more wary of government data collection. Today, 77% of Republicans say they are concerned about how the government uses data it collects about them, up from 63% four years earlier.
Privacy laws and regulation
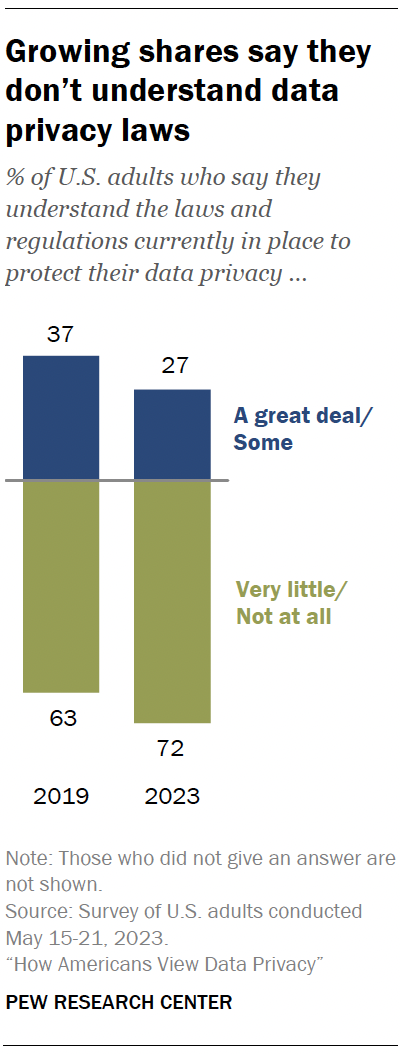
Americans are less knowledgeable about data privacy laws today than in the past.
Today, 72% of Americans say they have little to no understanding about the laws and regulations that are currently in place to protect their data privacy. This is up from 63% in 2019.
By comparison, the shares who say they understand some or a great deal about these laws decreased from 37% in 2019 to 27% in 2023.
Americans largely favor more regulation to protect personal information
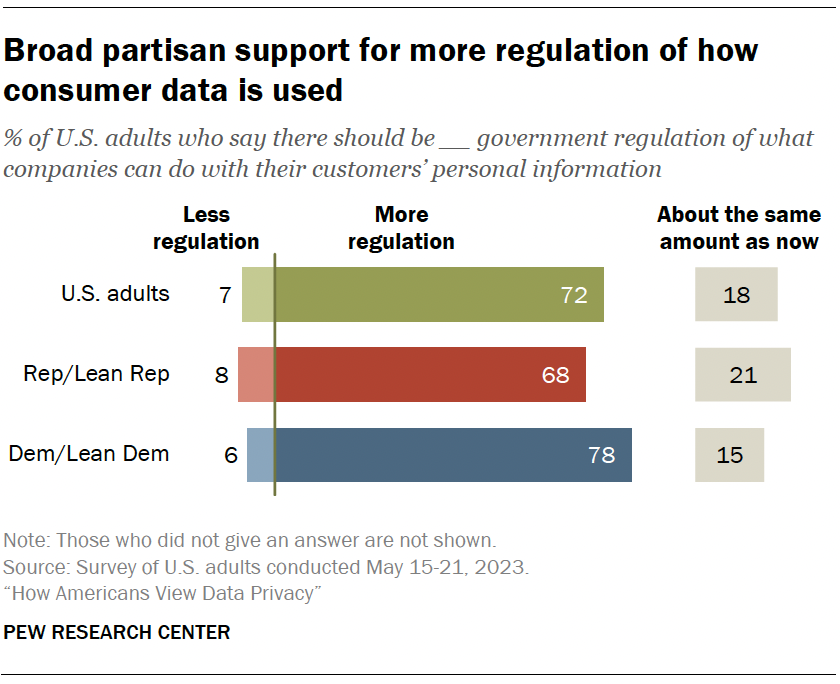
Overall, 72% say there should be more government regulation of what companies can do with their customers’ personal information. Just 7% say there should be less regulation. Another 18% say it should stay about the same.
Views by political affiliation
There is broad partisan support for greater involvement by the government in regulating consumer data.
A majority of Democrats and Republicans say there should be more government regulation for how companies treat users’ personal information (78% vs. 68%).
These findings are largely on par with a 2019 Center survey that showed strong support for increased regulations across parties.
Trust in social media executives
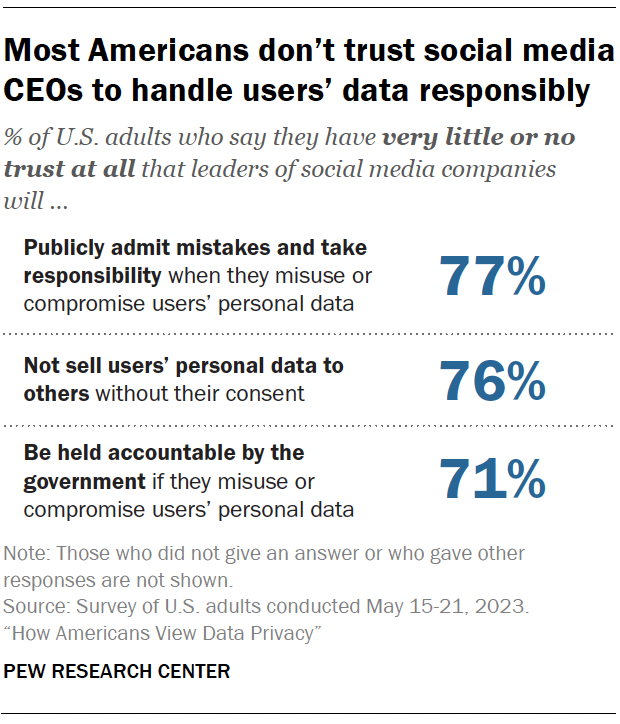
Majorities of Americans say they have little to no trust that leaders of social media companies will publicly admit mistakes regarding consumer data being misused or compromised (77%), that these leaders will not sell users’ personal data to others without their consent (76%), and that leaders would be held accountable by the government if they were to misuse or compromise users’ personal data (71%).
This includes notable shares who have no trust at all in those who are running social media sites. For example, 46% say they have no trust at all in executives of social media companies to not sell users’ data without their consent.
Children’s online privacy: Concerns and responsibility
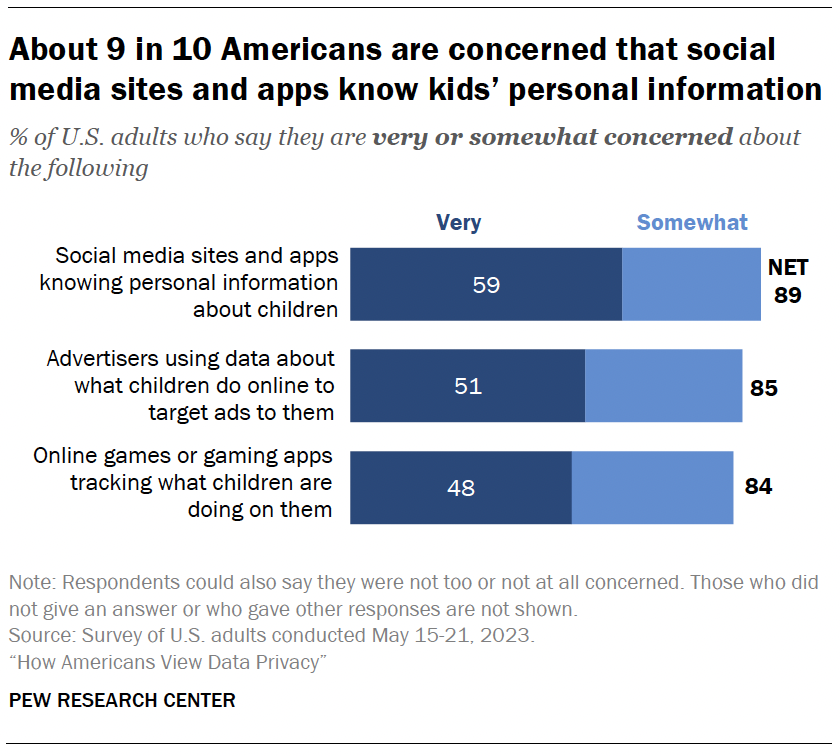
Most Americans say they are concerned about social media sites knowing personal information about children (89%), advertisers using data about what children do online to target ads to them (85%) and online games tracking what children are doing on them (84%).
Concern is widespread, with no statistically significant differences between those with and without children.
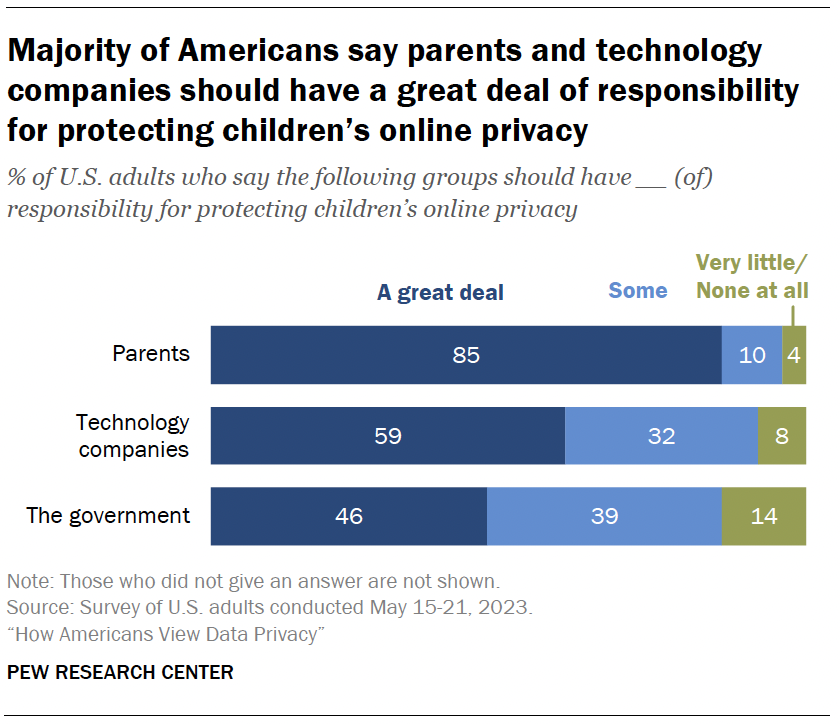
Another key question is who should be responsible for the actual protection of kids’ online privacy.
Fully 85% say parents bear a great deal of responsibility for protecting children’s online privacy. Roughly six-in-ten say the same about technology companies, and an even smaller share believe the government should have a great deal of responsibility.
Law enforcement and surveillance
The survey also measured how acceptable Americans think it is for law enforcement to use surveillance tools during criminal investigations.
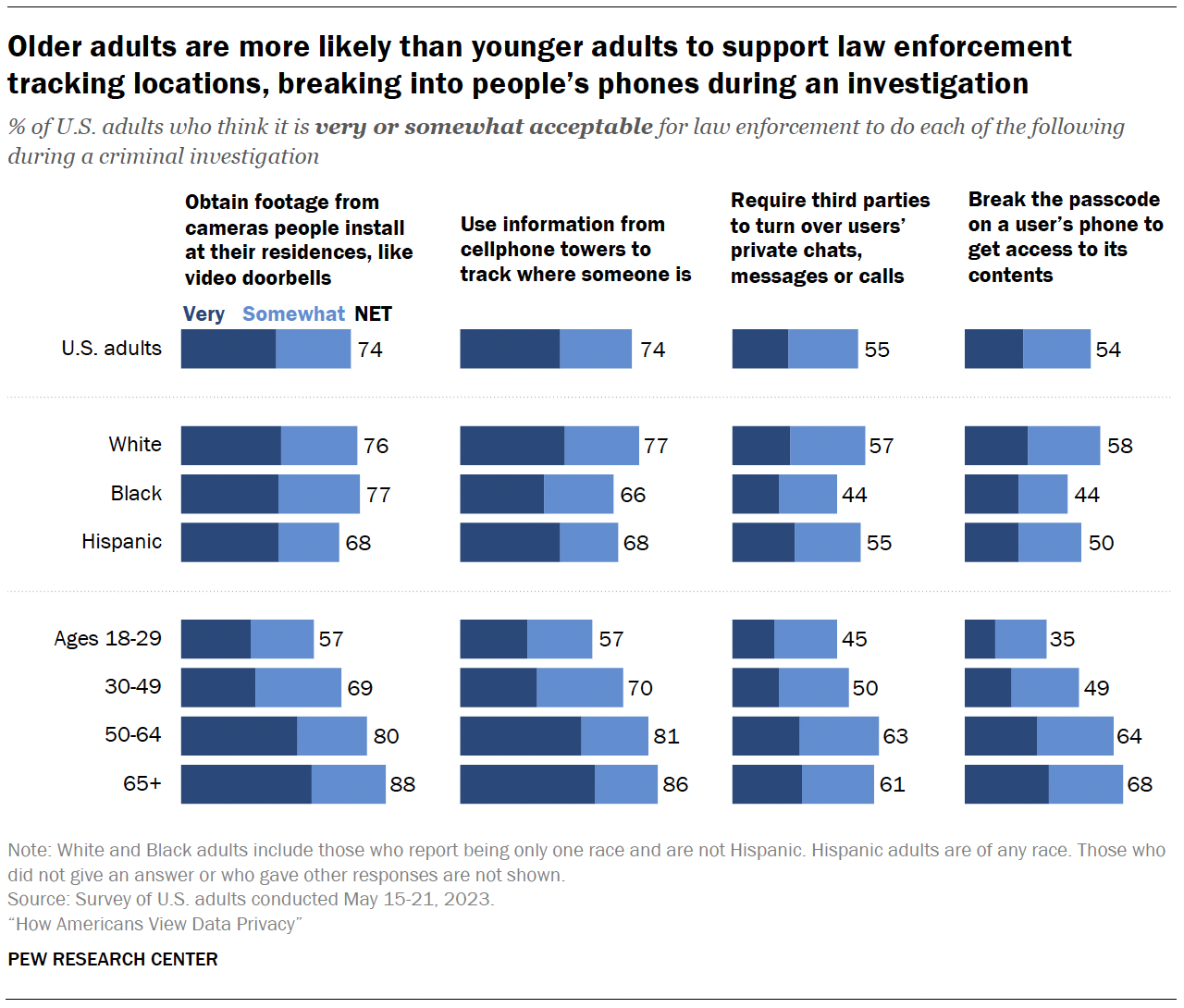
Roughly three-quarters of Americans say it’s very or somewhat acceptable for law enforcement to obtain footage from cameras people install at their residences during a criminal investigation or use information from cellphone towers to track where someone is.
By comparison, smaller shares – though still a slight majority – say it is acceptable to break the passcode on a user’s phone (54%) or require third parties to turn over users’ private chats, messages or calls (55%) during a criminal investigation.2
About one-in-ten Americans say they aren’t sure how they feel about law enforcement doing each of these things.
Age differences
Older adults are much more likely than younger adults to say it’s at least somewhat acceptable for law enforcement to take each of these actions in criminal investigations.
For example, 88% of those 65 and older say it’s acceptable for law enforcement to obtain footage from cameras people install at their residences, compared with 57% of those ages 18 to 29.
Racial and ethnic differences
In the case of a criminal investigation:
- White adults are more likely than Hispanic and Black adults to think it’s acceptable for law enforcement to use information from cellphone towers to track people’s locations and to break the passcode on a user’s phone to get access to its contents.
- White and Hispanic adults are more likely than Black adults to say it’s acceptable to require third parties to turn over users’ private chats, messages or calls.
AI and data collection
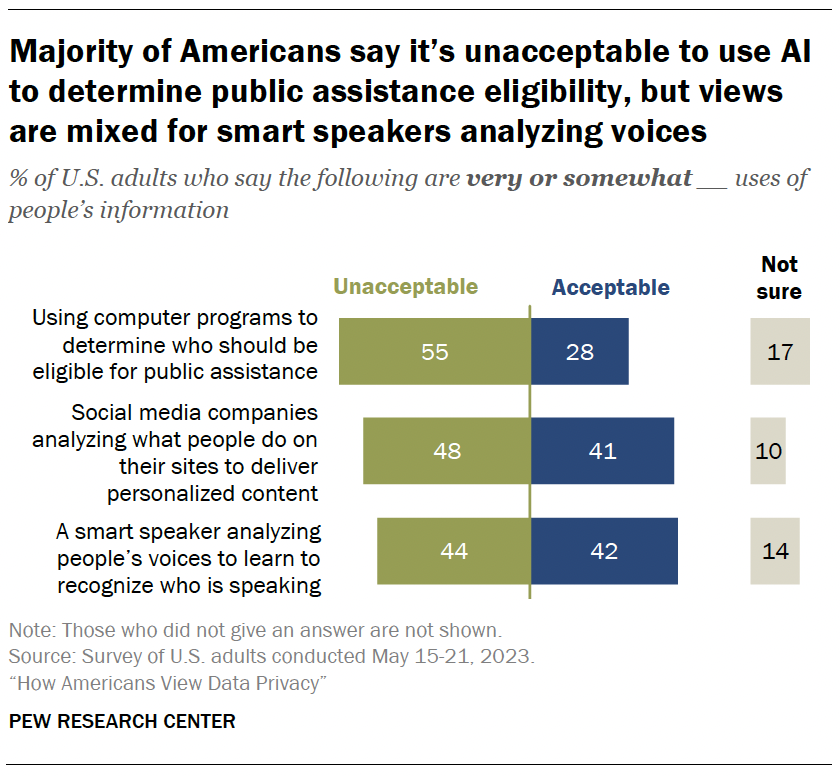
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to collect and analyze people’s personal information. Some Americans are wary of companies using AI in this way.
Fully 55% of adults say using computer programs to determine who should be eligible for public assistance is unacceptable. Roughly a quarter say it’s an acceptable use of AI.
Roughly half (48%) think it is unacceptable for social media companies to analyze what people do on their sites to deliver personalized content. Still, 41% are supportive of this.
Views are mixed when it comes to smart speakers analyzing people’s voices to learn who is speaking. Statistically equal shares say it’s unacceptable and acceptable (44% and 42%, respectively).
And some Americans – ranging from 10% to 17% – are uncertain about whether these uses are acceptable or not.
Age differences
- 49% of adults 50 and older say it’s unacceptable for a smart speaker to analyze people’s voices to learn to recognize who’s speaking. This share drops to four-in-ten among adults under 50.
- Similarly, 56% of those 50 and older say social media companies analyzing what people do on their sites to deliver personalized content is unacceptable. But 41% of those under 50 say the same.
- There are no differences between those under 50 and those 50 and older over whether computer programs should be used to determine eligibility for public assistance.
Trust in companies that use AI
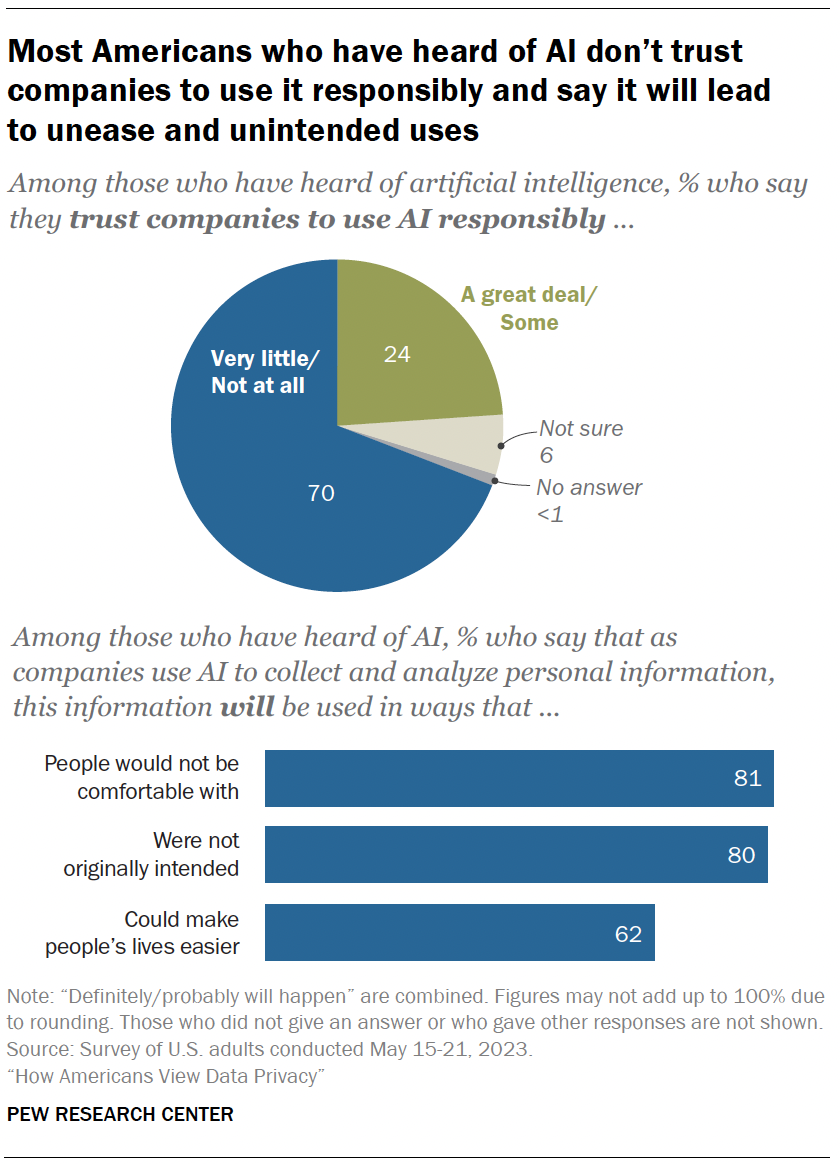
In addition to understanding people’s comfort level with certain uses of AI, the survey also measured the public’s attitudes toward companies that are utilizing AI in their products.
Among those who have heard of AI:
- 70% say they have little to no trust in companies to make responsible decisions about how they use AI in their products.
- Roughly eight-in-ten say the information will be used in ways people are not comfortable with or that were not originally intended.
- Views are more mixed regarding the potential that using AI to analyze personal details could make life easier. A majority of those who have heard of AI say this will happen (62%). Regarding differences by age, adults under 50 are more optimistic than those 50 and older (70% vs. 54%).
Education differences
Among those who have heard of AI:
- 87% of those with a college degree or higher say companies will use AI to analyze personal details in ways people would not be comfortable with. Some 82% of those with some college experience and 74% with a high school diploma or less say the same.
- 88% of those with a bachelor’s degree or more say companies will use this information in ways that were not originally intended. This share drops to 80% among those with some college experience and 71% among those with a high school diploma or less.
- About three-quarters of those with a college degree or more (74%) say this information will be used in ways that could make people’s lives easier. But this share drops to 60% among those with some college experience and 52% among those with a high school diploma or less.




