When it comes to tech adoption, seniors generally lag behind their younger counterparts. But for Americans ages 65 and older who own a smartphone, having one in their pocket is a liberating experience.
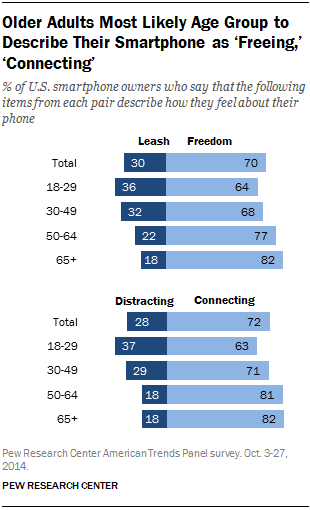
Asked if they feel that their phone represents “freedom” or “a leash,” 82% of smartphone-owning seniors described their phone as freeing, compared with 64% of those ages 18 to 29. By contrast, 36% of adult smartphone owners under the age of 30 described their phone as a leash, double the 18% of adults ages 65 and older who chose this term to describe their phone.
Similarly, when asked to describe their smartphone as “connecting” or “distracting,” older users are significantly more likely to choose “connecting” as the best descriptor. On the other hand, younger smartphone users are twice as likely as older adults to view their phone as “distracting” (37% vs. 18%).
Our survey did not directly ask why users chose the terms that they did, but differences in usage patterns may play a role. Younger adults tend to use their phones for a far wider range of purposes (especially social networking and multimedia content) and are much more likely to turn to their phone as a way to relieve boredom and to avoid others around them.
Older adults, by contrast, tend to use their phones for a narrower range of purposes – especially basic communication functions such as voice calling, texting and email. For young adults, smartphones are often the device through which they filter both the successes and annoyances of daily life – which could help explain why these users are more likely to report feeling emotions about their phone ranging from happy and grateful to frustrated or angry during a weeklong survey.
It is true, overall, that older Americans are less likely to be online, have broadband at home or own a mobile device. The same applies to smartphones: Only a quarter (27%) of adults ages 65 and older own them, compared with 85% of 18- to 29-year-olds, according to a Pew Research Center report released earlier this month.
A previous Pew Research study found that lower adoption rates of new technologies are often related to barriers seniors face when adopting them. These include medical conditions that make it difficult for older Americans to use certain technologies or devices. Skepticism about the benefits of technology and lack of digital literacy are other deterrents cited by older adults.
But that’s not to say older Americans aren’t broadening their digital experiences. In 2014, for the first time, more than half of online seniors indicated that they use Facebook: 56% of online adults ages 65 and older do so, up from 45% a year earlier. Internet use and broadband adoption continue to climb among older adults, and although there remains a wide age gap in smartphone ownership, the proportion of older adults who own a smartphone has increased by 8 percentage points since early 2014. Plus, older Americans who are internet adopters tend to have highly positive attitudes about the impact of online access on their lives, including the access that smartphones give them.