
The U.S. Constitution does not mention the Bible, God, Jesus or Christianity, and the First Amendment clarifies that “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion.” Still, some scholars have argued that the Bible heavily influenced America’s founders.
Today, about half of Americans (49%) say the Bible should have at least “some” influence on U.S. laws, including nearly a quarter (23%) who say it should have “a great deal” of influence, according to a recent Pew Research Center survey. Among U.S. Christians, two-thirds (68%) want the Bible to influence U.S. laws at least some, and among white evangelical Protestants, this figure rises to about nine-in-ten (89%).
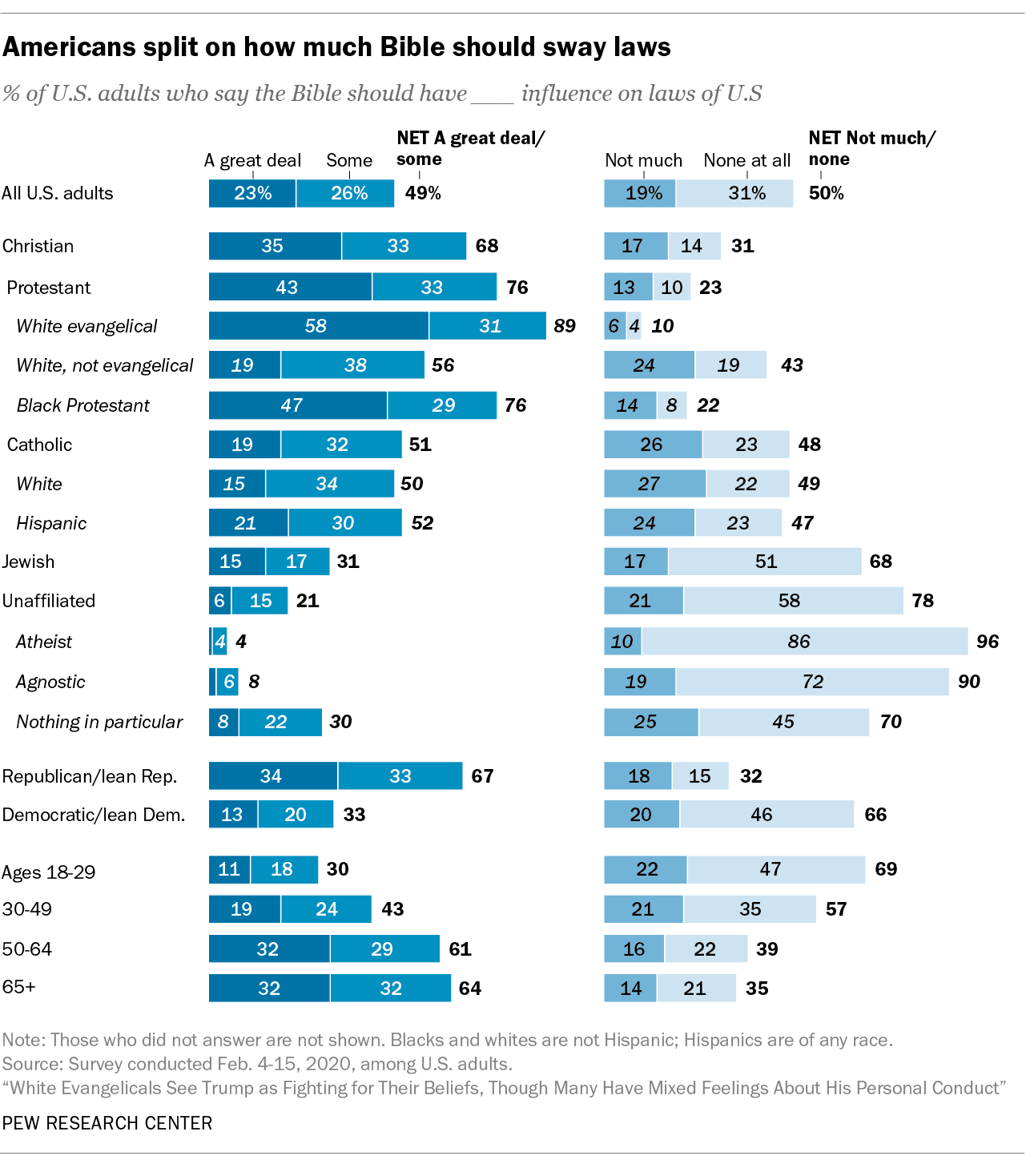
At the other end of the spectrum, there’s broad opposition to biblical influence on U.S. laws among religiously unaffiliated Americans, also known as religious “nones,” who identify as atheist, agnostic or “nothing in particular.” Roughly three-quarters in this group (78%) say the Bible should hold little to no sway, including 86% of self-described atheists who say the Bible should not influence U.S. legislation at all. Two-thirds of U.S. Jews, as well, think the Bible should have not much or should have no influence on laws.
How we did this
The findings in this post are drawn from a new survey exploring the intersection of religion and politics in the U.S. The survey of 6,395 U.S. adults was conducted Feb. 4 to 15. All respondents to the survey are part of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.
There also are differences on this question by age and political party. Older Americans are much more likely than younger adults to want biblical influence on U.S. laws, while Republicans – by a two-to-one margin – are more likely than Democrats to do so.
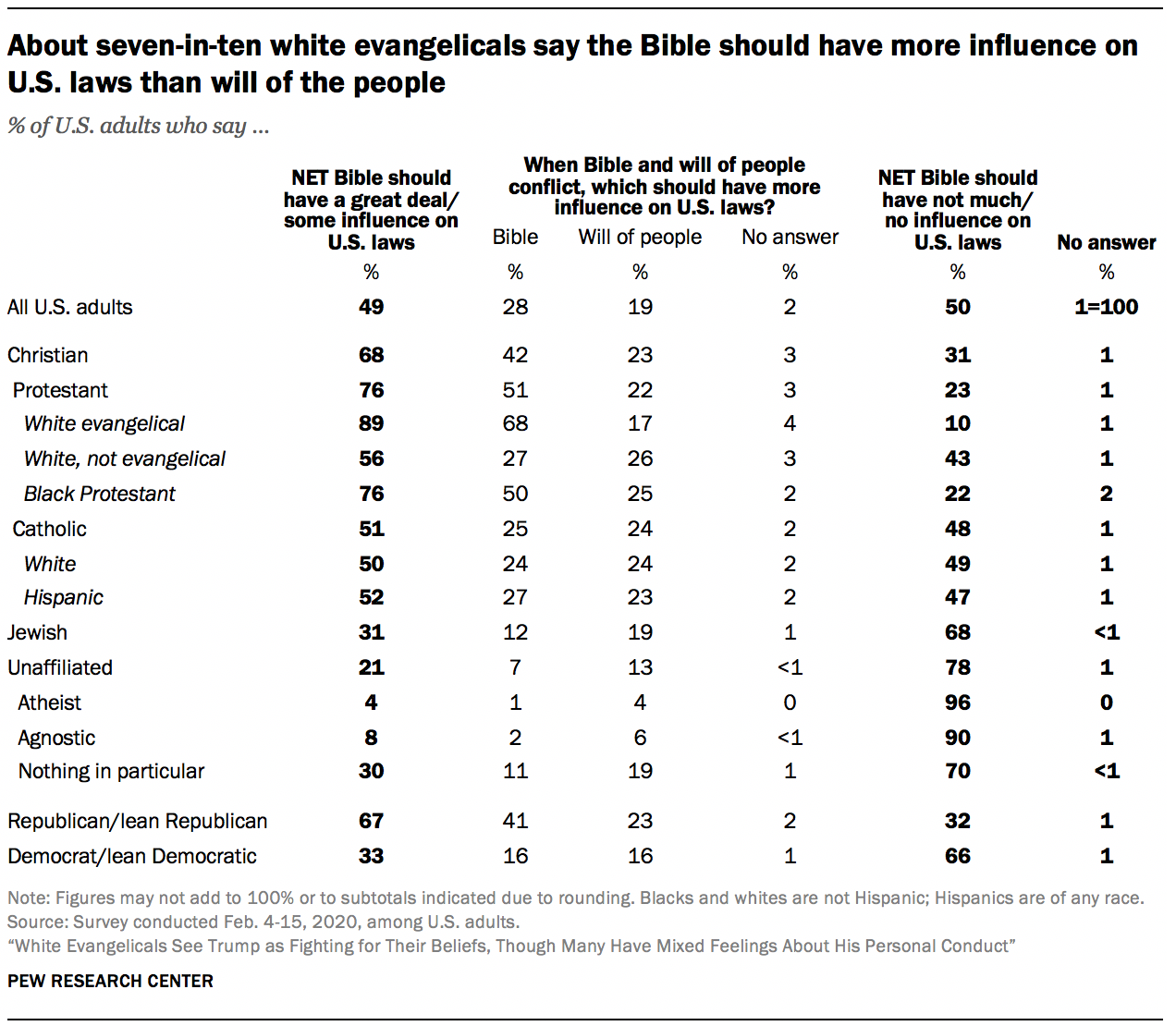
All survey respondents who said the Bible should have at least “some” influence on U.S. laws were asked a follow-up question: When the Bible and the will of the people conflict, which should have more influence on U.S. laws?
The more common answer to this question is that the Bible should take priority over the will of the people. This view is expressed by more than a quarter of all Americans (28%). About one-in-five (19%) say the Bible should have at least some influence but that the will of the people should prevail.
Two religious groups stand out for being especially supportive of biblical influence in legislation, even if that means going against the will of the American people: Two-thirds of white evangelical Protestants (68%) say the Bible should take precedence over the people, and half of black Protestants say the same. Among Catholics (25%) and white Protestants who do not identify as born-again or evangelical (27%), only about a quarter share this perspective.
The survey did not ask people what they had mind when thinking of biblically influenced laws. It’s possible some were thinking of “biblical marriage,” defined by some Christian leaders as a marriage between one man and one woman, precluding same-sex unions. Recent surveys by the Center find that most white evangelical Protestants (63%) and half of black Protestants (50%) continue to oppose legal same-sex marriage.
Note: Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.