This analysis is based on 1,314 school district mission statements that are publicly available on school district websites. The data was collected by searching the websites of 1,500 regular public school districts. School districts across the country may label or describe their mission statements using a variety of different terms. For the purposes of this analysis, mission statements are defined as public statements on school district websites that define and reflect the district’s role in education and its prioritized goals for educating students. Only mission statements published on school district websites as of November 2022 are included; statements published on the websites of individual schools located within that district are excluded.
The study population is defined based on the list of all regular public school districts in the United States available at the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) website, excluding those not found on the U.S. Census Bureau data platform and those with missing student registration information. From this initial list of 12,728 districts, researchers randomly selected a list of 1,500 regular public school districts stratified by urbanicity level (with 500 districts each from urban, suburban and rural areas).
Data collection
Three researchers manually searched online to find the websites of these 1,500 districts and manually collected documents from each website meeting the definition of a “mission statement” noted above. If a statement was available in an image format on the website, it was transcribed before being added to the dataset. If multiple webpages on a district’s website contained a mission statement, the different pages were combined and analyzed as a single document.
Of the initial 1,500 school districts, 12% in total either had no publicly available website (n=13) or had a website but no available mission statement (n=173) and were excluded from the analysis. The remaining 1,314 documents form the basis of this analysis. Data was collected Nov. 16-28, 2022, and may not reflect changes to mission statements that have taken place since then.
Population data and median household income data for U.S. school districts comes from the 2015-2019 American Community Survey estimates published by the Census Bureau (accessed through the tidycensus package in R). The median income variable is adjusted for regional differences, using regional price parities by state and metro area, available at the Bureau of Economic Analysis website. Information on whether the districts are in urban, suburban or rural areas is collected from the NCES website.
Vote shares for each school district from the 2020 general election are calculated using 2020 General Election Results Disaggregated to 2020 Census Blocks Datasets available at the Redistricting Data Hub website. This block-level data was aggregated up to the school district level, using block-to-school district relation files from Missouri Census Data Center’s Geographic Correspondence Engine (Geocorr 2022).
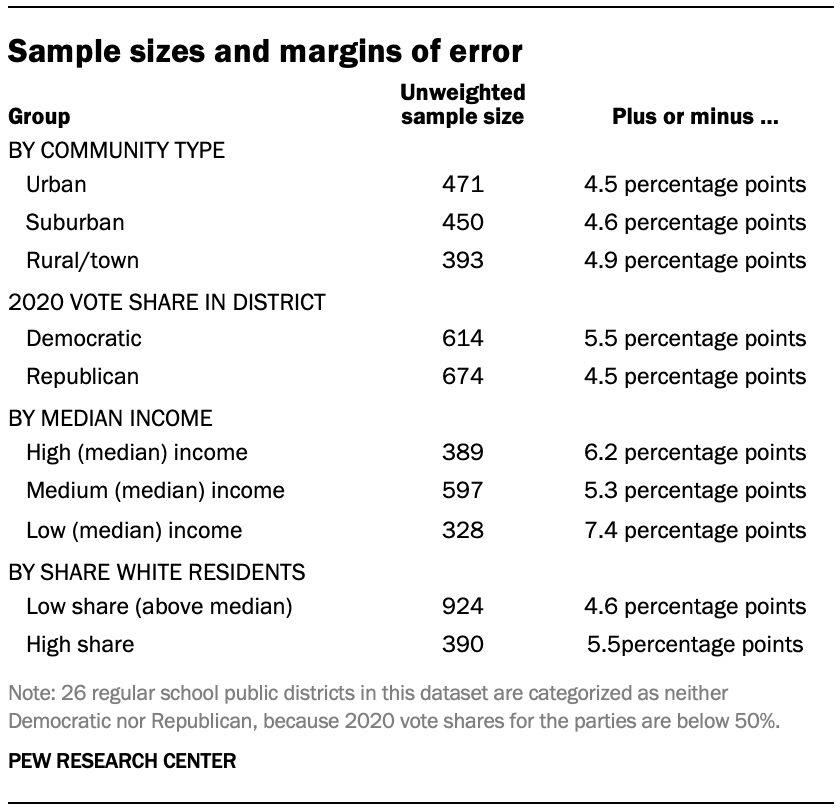
Any statements pertaining to all school districts in the analysis have a margin of error of 3.6 percentage points at a 95% confidence level. The following table shows the unweighted sample sizes and the error attributable to sampling that would be expected at the 95% level of confidence for different demographic groups in the analysis.
Coding
Two researchers were assigned to code the collected mission statement texts using the following coding guidelines. These topics are not mutually exclusive – documents could be classified into multiple categories.
Academic skills
Definition
Academic skills that students are expected to achieve during their education.
Example terms
academic skills; problem solving; analytical thinking; critical thinking; acquiring knowledge; creativity/creative thinking; curricular skills; technical skills; acquiring knowledge; literacy; digital/technological skills; computer skills
Exclusions
general emphasis on skills; academic support/needs/ development/expectations; academic success/growth (as it is hard to differentiate between personal academic skills vs. school success)
Future readiness
Definition
Preparing students to become a citizen/member of society; students’ civic engagement with the community.
Example terms
citizenship; becoming a member of society; lifelong learners; 21st-century skills; students as productive members of community; college-ready; job market ready; preparing for life
Exclusions
future-ready facilities (refers to the district, not student readiness); terms such as “student success”
Academic program and excellence
Definition
Academic performance/rigorousness of the district and/or the students. This also includes district ranking and/or mentions of curriculum and coursework.
Example terms
academic excellence/performance/expectations; [innovative] academic program; student’s academic learning outcome; leading program; top-ranking program; coursework; curriculum; improving test scores; science; arts
Exclusions
stand-alone verbs like succeed, empower; nouns such as growth, achievement (such as educational success/excellence) unless they specifically refer to “academic”; references to staff or teachers (instead of the academic program); academic support/needs/development (as it is hard to differentiate between personal academic skills vs. school success); academic success/growth (hard to differentiate between personal academic skills vs. school success)
Safe and healthy environment
Definition
General or specific references to safe and/or healthy environment/school culture/community; supportive and caring school/district environment.
Example terms
safe/healthy/positive environment; drug-safe; gun-safe; [the school/district] fostering nurturing/caring relationships; respectful environment; an environment without fear; providing support/wellness to students; welcoming environment
Exclusions
healthy behaviors of students; any emphasis to “social-emotional” (as that might refer to student skills and therefore gets ambiguous)
Diversity, equity and inclusion
Definition
Inclusion/equity/diversity of demographic/cultural groups; includes mentions of closing the achievement gap or similar wording.
Example terms
inclusion/equity/diversity; [respecting] cultural differences; multiculturality; multilinguality; celebrating diversity; culturally responsive teaching; diverse world; meeting needs regardless of student disability/socioeconomics/etc.; closing the achievement gap; equal opportunity
Exclusions
None
Parent and community involvement
Definition
Districts working inclusively with other members of the community, including organizations and families of the students.
Example terms
engaging families and community [in education]; [educating] in collaboration with families and community; parents/community commitment in education
Exclusions
students’ collaboration with each other as a part of their social skills; district informing families/community
Student-centered education
Definition
Districts emphasizing personalized education or their education designed to be centered around students’ dreams, aspirations, personalities.
Example Terms
student-oriented/student-centered [education]; considering students’ aspirations/expectations; authenticity of the education; amplifying student voice; responsive/differentiated teaching
Exclusions
Phrases such as “every/all/each student,” “meeting individual needs,” “meeting each student’s needs” (as it is unclear whether the district defines those needs as individualized)
Mental health
Definition
Detecting/addressing/assessing students’ mental health.
Example terms
[provide] mental health [services]
Exclusions
terms such as “safe space” or “wellness” that are unclear whether they refer to mental or physical health; or school safety in general (those go under “safe/healthy”); mental skills (as they tend to refer to student development)
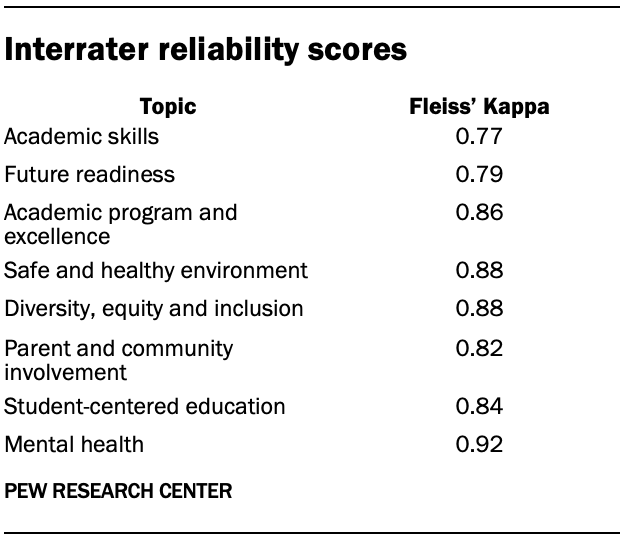
The following table shows the Fleiss’ Kappa score for each of these eight topics, which is a measure of interrater reliability.
Identifying topic-related distinctive terms
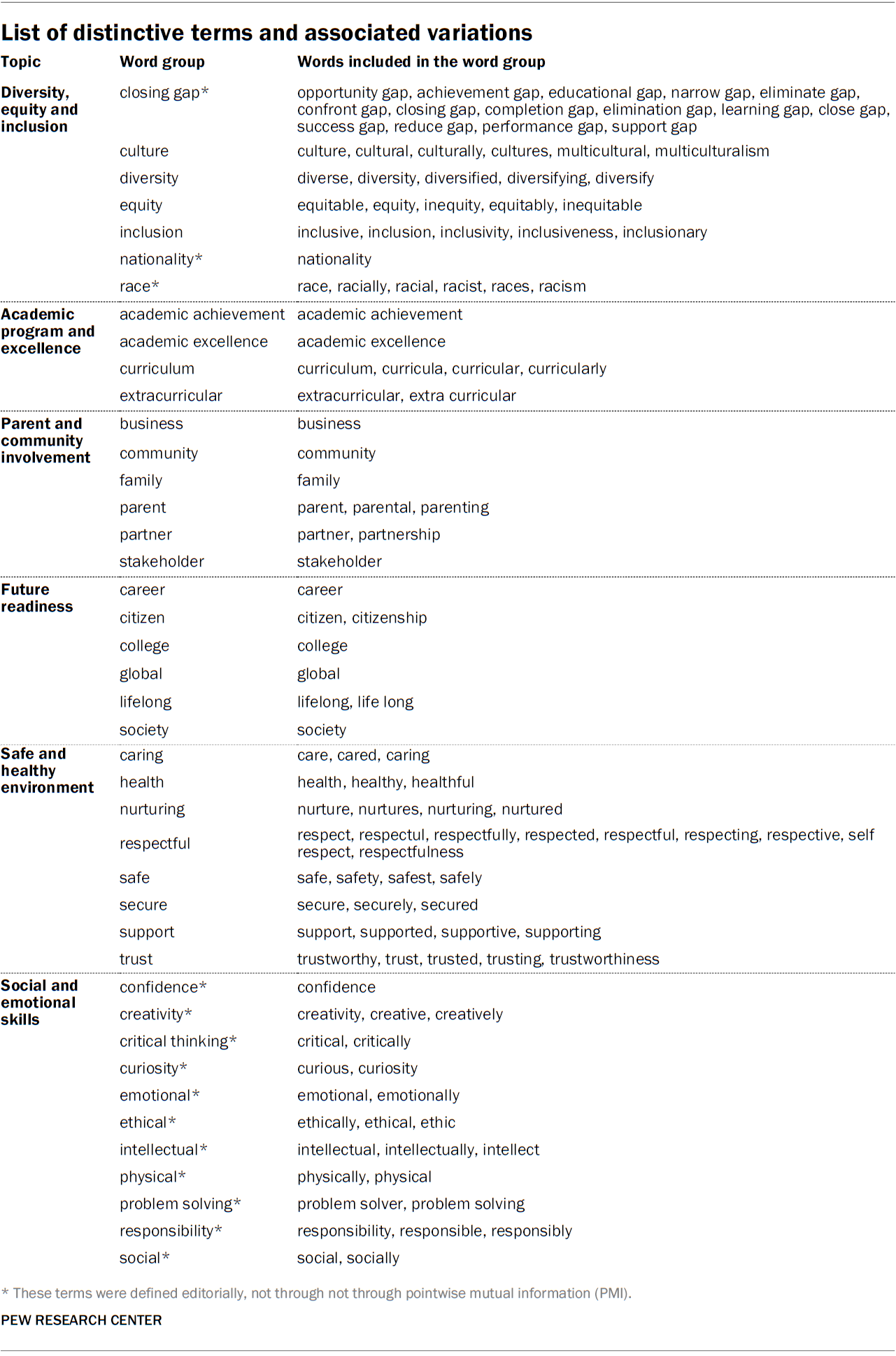
Researchers identified distinctive terms related to the topics defined in the qualitative coding rubric using pointwise mutual information (PMI). For each identified distinctive term, regular expressions were used to identify all variations of the term appearing in these documents. For example, “culture” is one of the distinctive terms related to diversity, equity and inclusion based on PMI. Other terms with the same root (such as “cultural” or “culturally”) were then added to the term group “culture,” prior to running the word count analysis.
Researchers also included a small number of additional terms (apart from the PMI-identified ones) that they considered relevant to the topic in question. The full list of terms and their associated group of terms are listed in the table below, and terms not identified using the PMI method are marked with an asterisk.
Word-count analysis
For the full list of identified terms, the word count analysis identifies the share of mission statements that includes the term. While calculating shares, the analysis looks at whether a certain term (and its variations included in the term-group) appears in a mission statement or not, instead of counting the number of times this term appears in mission statement texts.




