
Last year, Google introduced “AI Overviews,” a feature that displays an artificial intelligence-generated result summary at the top of many Google search pages. This feature is available to millions of U.S. Google users. Online publishers recently have attributed declining web traffic to these summaries replacing traditional search results, claiming that many users are relying on the summaries instead of following links to the publishers’ websites.
A Pew Research Center report published this spring analyzed data from 900 U.S. adults who agreed to share their online browsing activity. About six-in-ten respondents (58%) conducted at least one Google search in March 2025 that produced an AI-generated summary. Additional analysis found that Google users were less likely to click on result links when visiting search pages with an AI summary compared with those without one. For searches that resulted in an AI-generated summary, users very rarely clicked on the sources cited.
Here’s more of what we learned about Google AI summaries and how users interact with them.
Google users who encounter an AI summary are less likely to click on links to other websites than users who do not see one. Users who encountered an AI summary clicked on a traditional search result link in 8% of all visits. Those who did not encounter an AI summary clicked on a search result nearly twice as often (15% of visits).
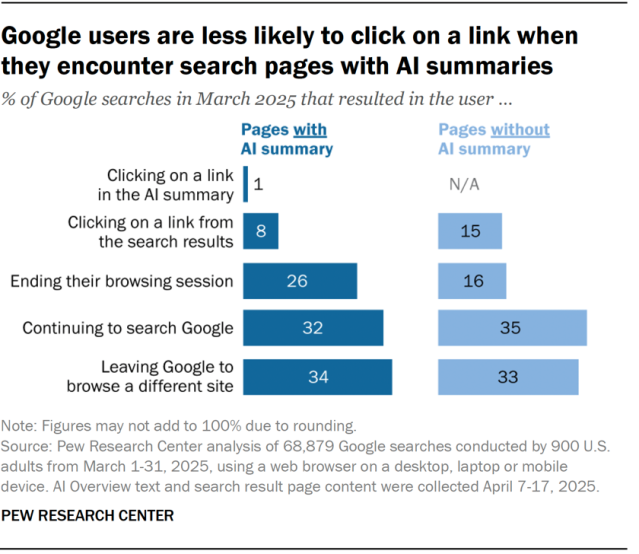
Google users who encountered an AI summary also rarely clicked on a link in the summary itself. This occurred in just 1% of all visits to pages with such a summary.
Google users are more likely to end their browsing session entirely after visiting a search page with an AI summary than on pages without a summary. This happened on 26% of pages with an AI summary, compared with 16% of pages with only traditional search results.
Regardless of whether a page had an AI-generated summary or not, the largest share of Google searches in our study resulted in the user either browsing elsewhere on Google or leaving the site entirely without clicking a link in the search results. Around two-thirds of all searches resulted in one of these actions.
The most frequently cited sources in both Google AI summaries and standard search results are Wikipedia, YouTube and Reddit. These three sites are the most commonly linked sources in AI summaries and standard search results alike. Collectively, they accounted for 15% of the sources that were listed in the AI summaries we examined. They made up a similar share (17%) of the sources listed in standard search results.
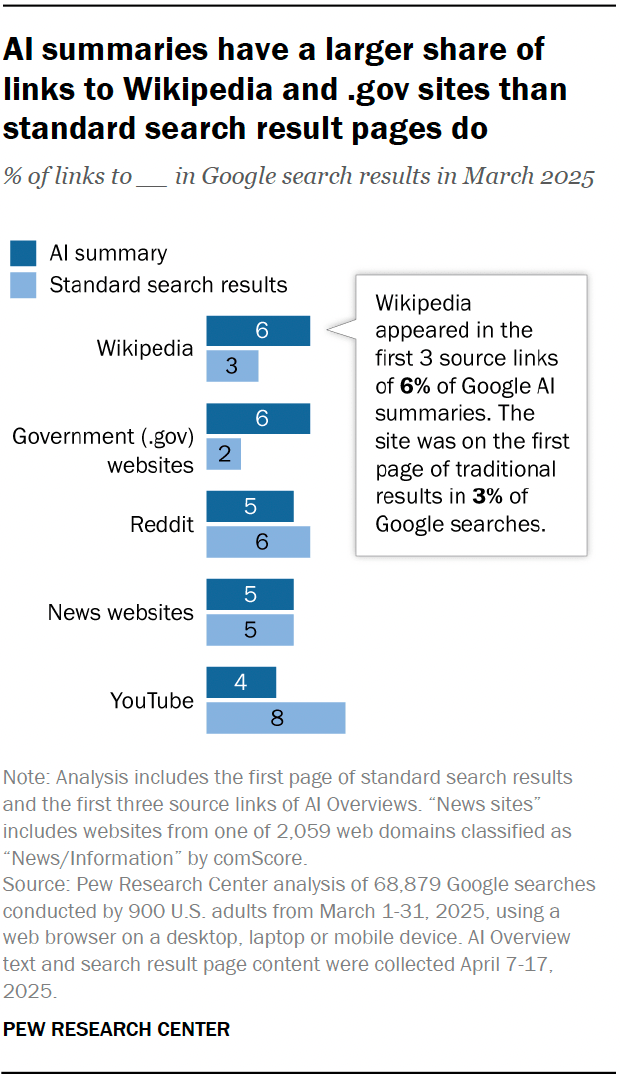
Wikipedia links are somewhat more common in AI summaries than in standard search pages, while YouTube links are somewhat more common in standard search results than in AI summaries.
When it comes to the type of websites that are often linked to in Google search results, government websites are more common in AI summaries than in standard search results. Some 6% of the sources that were linked in AI overviews were to .gov websites, compared with just 2% for standard search results. Meanwhile, 5% of AI summaries – and 5% of standard search results – linked to news websites.
Overall, around one-in-five Google searches in March 2025 produced an AI summary. Some 18% of all the Google searches in our study generated an AI summary as part of the search results. The vast majority of these summaries (88%) cited three or more sources. Only 1% cited a single source.
The typical (median) AI summary in our study was 67 words long, but this varied widely. The shortest we found was just seven words long, while the longest ran to 369 words.
Google searches that contain more words, ask questions or use full sentences tend to produce AI summaries more often. Longer searches are more likely to produce an AI summary. Just 8% of one- or two-word searches resulted in an AI summary. But that share rose to 53% for searches with 10 words or more.
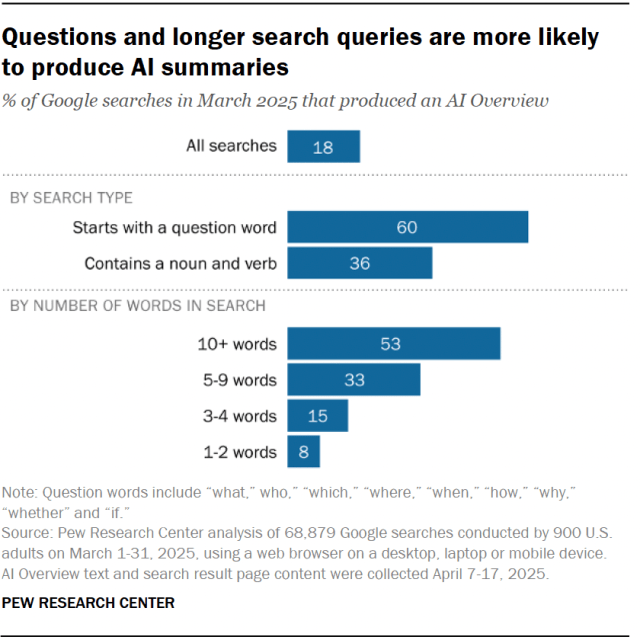
Other types of searches that tend to result in AI summaries include:
- Searches that form questions: 60% of search queries that began with question words such as “who,” “what,” “when” or “why” resulted in an AI summary.
- Searches that use full sentences: 36% of searches that include both a noun and a verb generated an AI summary.

