Social media plays a crucial role in Americans’ news consumption. Half of all U.S. adults say they at least sometimes get news there, according to a 2023 Pew Research Center survey.
Those who get news on social media name a variety of things that they like about it, including convenience, speed and the element of social interaction. But some social media news consumers also express concerns about news there being inaccurate, low quality and politically biased. The share who say inaccuracy is the aspect they dislike most has increased from 31% to 40% in the past five years.
These findings come from a broader Center survey of U.S. adults’ news habits. The survey asked Americans who get news on social media to describe – in their own words – the things they like and dislike most about getting news there. Their responses were then sorted into categories.
Pew Research Center asked two open-ended questions about what people like and dislike most about getting news on social media as part of a survey on U.S. adults’ news habits. The survey of 8,842 U.S. adults was conducted from Sept. 25 to Oct. 1, 2023.
Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
We asked all respondents who say they get news on social media to answer the open-ended questions. Responses were manually coded into categories. In total, we coded 4,507 open-end responses on what respondents like the most and 4,453 responses on what respondents dislike the most.
Here are the questions used for the fall 2023 survey, along with responses, and its methodology.
We asked whether Americans prefer social media or news outlets for various types of information on a separate ATP survey conducted March 20-26, 2023, among 3,576 U.S. adults. Here are the questions used for the spring 2023 survey, along with responses, and its methodology.
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. This is the latest report in Pew Research Center’s ongoing investigation of the state of news, information and journalism in the digital age, a research program funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation.
What Americans like about getting news on social media
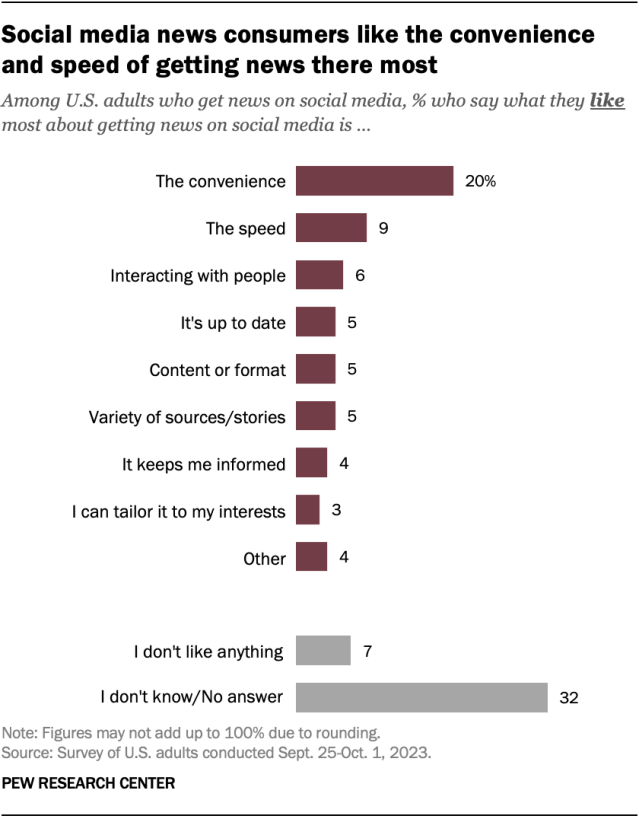
The aspects of getting news on social media that Americans value have not changed much since 2018, the last time we asked these questions. Convenience remains the top thing people like most about getting news on social media. One-in-five social media news consumers say this, with responses such as “It’s at my fingertips,” “I can easily get it” and “It’s available all the time and anywhere.”
Another 9% say they like the speed with which they can get news there, describing news on social media as “fast and to the point” and “quick and easy to digest.”
Smaller shares say they like interaction with others, the up-to-date nature of the news, the content or format, and the variety of sources and stories.
Meanwhile, 7% of Americans who get news on social media say they don’t like anything about the experience, and an additional 32% did not offer a response.
What Americans dislike about getting news on social media
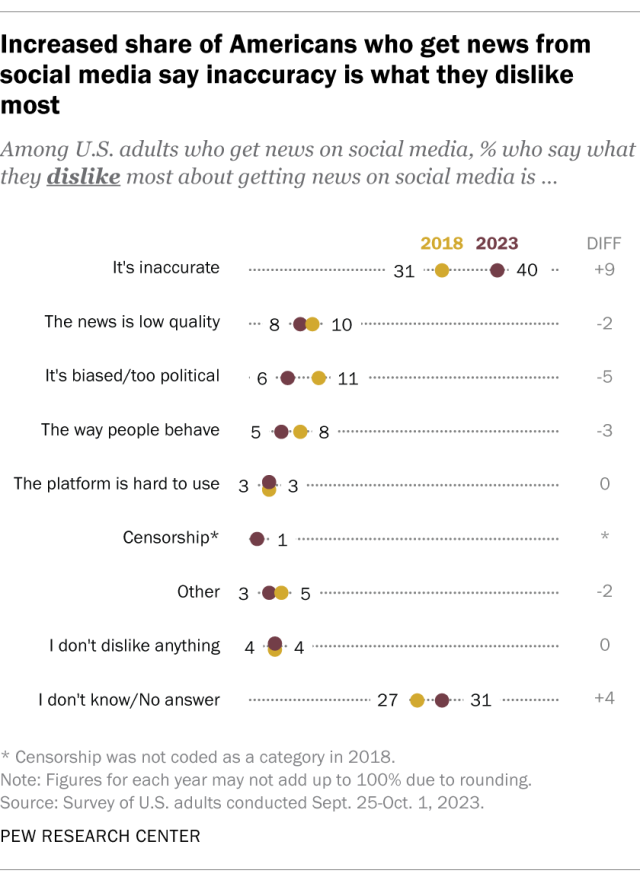
Many social media news consumers also see downsides to getting news this way. Four-in-ten Americans who get news from social media say inaccuracy is the thing they dislike most about it – an increase of 9 percentage points since 2018. This category of responses includes concerns about unverified facts, misinformation, “fake news” and unreliable sources.
A much smaller share of social media news consumers (8%) say they dislike the low quality of news there, with some giving clickbait or a lack of in-depth coverage as examples. Others say the news on social media is too biased or political (6%) or they don’t like the way people behave there (5%).
Another 1% of social media news consumers say censorship is what they dislike most. This category – which we used for the first time in the 2023 survey – includes responses such as “Too much censorship by the sites” and “I really dislike when some of my view points are removed.” There are no significant differences in the shares of Democratic and Republican social media news consumers who say they’re concerned about news censorship on social media. In fact, there are no partisan differences within any of these complaint categories.
Just 4% of respondents say they don’t dislike anything about getting news on social media. Another 31% did not answer the question.
Social media posts versus news outlets: Which do Americans prefer for certain types of information?
The perceived downsides of getting news on social media may help explain why many Americans prefer to go directly to news outlets instead. In a separate Center survey, U.S. adults who say they at least sometimes get news on social media were asked whether they prefer reading social media posts or going directly to news outlets for five different types of information. Those types of information include the basic facts about an issue or event as well as in-depth information and opinions on it.
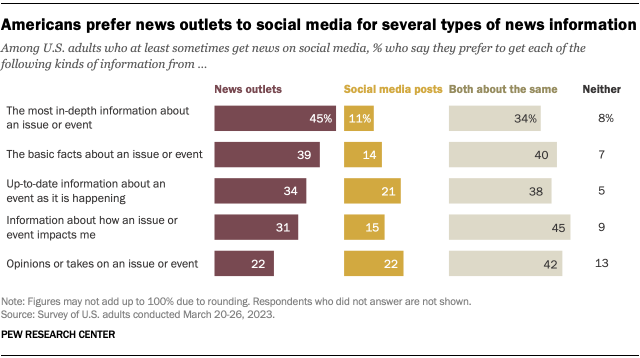
Americans prefer to get four of the five types of information from news outlets over social media. However, a substantial share say they like getting each type of information from news outlets and social media about the same.
For example, 45% of respondents say they prefer news outlets for getting the most in-depth information about an issue or event, while only 11% prefer social media posts for this. An additional 34% say they value both sources equally, while 8% say they prefer neither option.
Social media news consumers also tend to prefer news outlets over social media to get:
- The basic facts about an issue or event (39% vs. 14%)
- Up-to-date information about an event as it is happening (34% vs. 21%)
- Information about how an issue or event impacts them (31% vs. 15%)
In each of these cases, roughly four-in-ten or more say they like social media and news outlets about the same.
In contrast, equal shares of Americans prefer news outlets and social media when it comes to opinions on an issue (22% each).
Previous Center research has shown that younger Americans are more likely than older Americans to prefer getting news from social media, and that pattern also appears in the findings of this survey. Adults under 30 express a clear preference for using social media over news outlets to get opinions on an issue (36% vs. 13%) and up-to-date information as an event is happening (35% vs. 21%). Americans ages 65 and older are much more likely to prefer news outlets over social media for every type of information we asked about.
