
Note: For the latest survey data on views of the European Union, read our 2022 post.
Majorities across much of Western Europe, North America and the Asia-Pacific region have a favorable view of the European Union, according to a recent Pew Research Center survey of 17 advanced economies. But perceptions of the EU’s response to the coronavirus outbreak are mixed, and while many in Europe say economic relief from the Brussels-based institution has been sufficient, substantial shares in most countries feel it has not gone far enough.
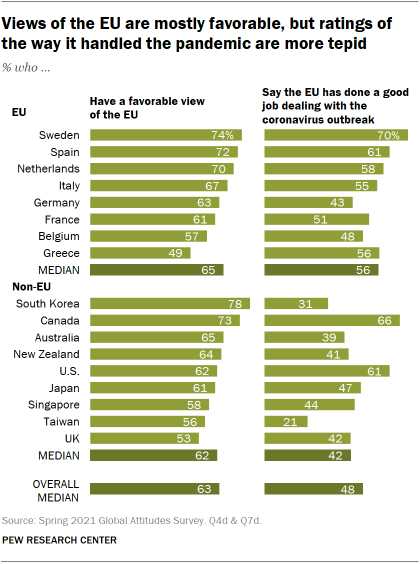
A median of 63% across the 17 publics surveyed rate the EU positively. Among the eight member states surveyed, opinions are most favorable in Sweden, Spain and the Netherlands, where at least 70% have a positive view of the EU.
These three countries also have the most positive evaluation in the region of the EU’s response to the pandemic; roughly six-in-ten or more say the organization has done a good job handling the coronavirus outbreak. By comparison, a median of only 48% across all 17 publics approve of the EU’s response.
This analysis focuses on public opinion of the European Union, including views of the EU’s response to the coronavirus outbreak. For non-U.S. data, the report draws on nationally representative surveys of 16,254 adults from March 12 to May 26, 2021, in 16 publics. All surveys were conducted over the phone with adults in Canada, Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, the UK, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan.
In the United States, we surveyed 2,596 U.S. adults from Feb. 1 to 7, 2021. Everyone who took part in the U.S. survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
To account for the fact that some publics refer to the coronavirus differently, in South Korea, the survey asked about the “Corona19 outbreak.” In Japan, the survey asked about the “novel coronavirus outbreak.” In Greece, the survey asked about the “coronavirus pandemic.” In Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Taiwan, the survey asked about the “COVID-19 outbreak.” All other surveys used the term the “coronavirus outbreak.”
Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses. See our methodology database for more information about the survey methods outside the U.S. For respondents in the U.S., see our U.S. survey methodology. Information on populist party categorization can be found here.
Although majorities in Germany, France and Belgium have a positive assessment of the EU overall, only about half or fewer think it has handled the outbreak well. Greeks are the least likely among those surveyed to view the EU favorably overall, though a majority of Greeks say the EU did well in its response to the pandemic.
The EU’s economic response to the pandemic generally receives mixed reviews from the European countries polled. When thinking about the economic consequences of the coronavirus, a median of 48% say the EU’s relief efforts have been about right, compared with 40% who say they have not gone far enough and just 6% who think they have gone too far. Here again, people in Sweden and the Netherlands have some of the most positive assessments of the EU, while those in Greece say the EU’s economic efforts are insufficient.
Outside the EU, many express a positive opinion of the institution, while Canadians and Americans also rate the EU’s response to the outbreak positively. Roughly six-in-ten Americans have a positive view of the EU and say it did a good job in response to the pandemic. But relatively few in the Asia-Pacific region approve of how the EU has handled the outbreak. Only 39% in Australia, 31% in South Korea and 21% in Taiwan think the EU did well in its response.
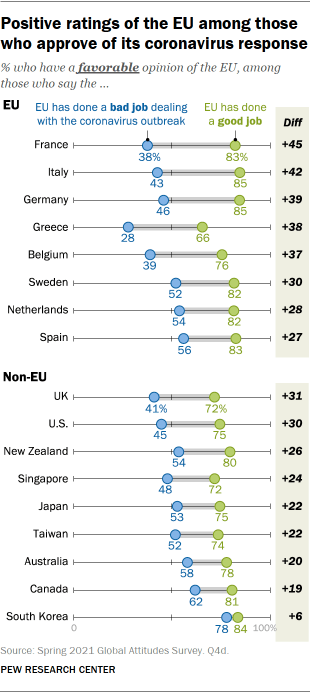
The sense that the EU has handled the pandemic well is related to positive assessment of the EU in every public surveyed. In France, for example, 83% of those who think the EU handled the outbreak well view the institution favorably, compared with only 38% who think the EU did a bad job dealing with the outbreak. Differences in EU favorability based on how people view its pandemic response tend to be larger in most EU countries surveyed, compared with publics in the Asia-Pacific region.
Similarly, people in the eight EU countries surveyed who rate the EU’s economic response to the outbreak positively are much more likely to express a positive opinion of the organization than those who think economic relief efforts did not go far enough.
Despite more mixed ratings of the EU’s coronavirus response, overall opinion of the EU has been at its highest in recent years in several countries. Favorable views of the EU in Italy and Sweden saw significant increases since last year, with two-thirds or more in each country now viewing the EU positively. Japan and South Korea also saw similar increases, with Japan going from an all-time low of 47% in 2020 to 61% this year.
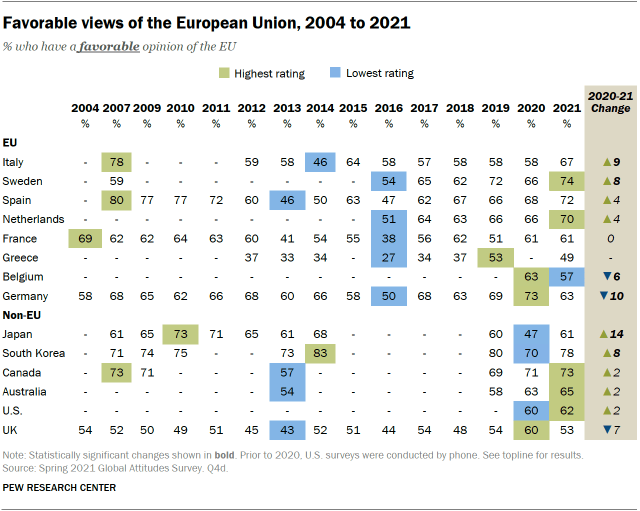
On the other hand, there were also notable decreases in public approval of the EU. Belgium and Germany both saw significant decreases in approval of the EU, with Germany dropping from a high of 73% in 2020 to 63% this year. There was a similar drop in the UK, where ratings of the institution were at a historic high in 2020 after the country officially left the EU, though roughly half still have a positive opinion.
Within the publics surveyed, there are considerable divides in approval of the EU across age, education and political groups. Adults ages 18 to 29 are significantly more likely to approve of the EU than those 65 and older in 10 publics, including the UK, France, Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands. In France, for example, 80% of younger adults approve of the EU, while just 57% of older adults say the same – a 23 percentage point difference.
Similar divides can be seen across education levels in 11 of the publics surveyed. Those who have a postsecondary degree are more likely to approve of the EU. In the UK, for example, 65% of those with higher levels of education are warm to the EU, compared with 46% of those with a secondary degree or less.
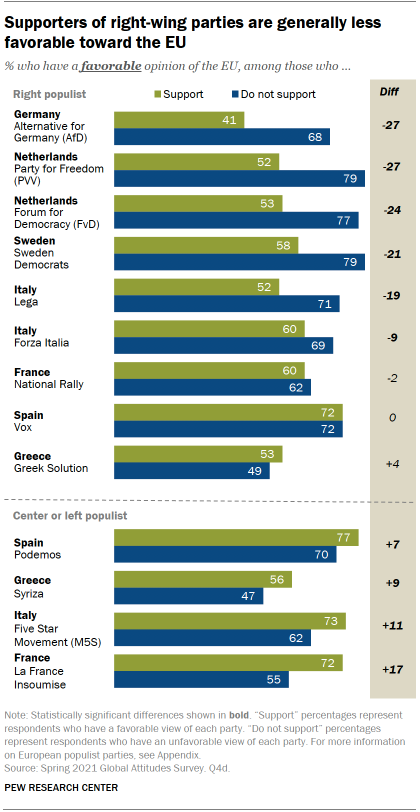
Ideology and party backing are often tied to assessment of the EU within the member countries surveyed. In general, supporters of right-wing populist parties are notably less supportive of the EU. This pattern can be seen in Italy, Sweden, the Netherlands and Germany. For example, while 68% of those who do not support Alternative for Germany (AfD) approve of the EU, only 41% of AfD supporters say the same. The opposite pattern can be seen among the center and left-wing populist parties in Europe, where supporters of these parties are more likely to have a positive assessment of the EU.
Ideology is related to views of the EU outside the bloc as well. People who place themselves on the left of the political spectrum are significantly more likely than those who place themselves on the right to evaluate the EU positively in the UK, Australia, New Zealand and Canada. In the U.S., Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents have more positive opinions of the EU (78%) than Republicans and Republican-leaning independents (46%).
Note: Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses, and its U.S. methodology and full dataset.
