The analysis in this report is based on a nationally representative online survey conducted by Pew Research Center Jan. 3-13, 2020, among a sample of 3,535 adults 18 years of age or older residing in the United States. This included an oversample of 175 U.S.-born Hispanics and 243 foreign-born Hispanics. The survey was conducted by Ipsos Public Affairs in English and Spanish using KnowledgePanel, its nationally representative online research panel.
KnowledgePanel members are recruited through probability sampling methods and include both those with internet access and those who did not have internet access at the time of their recruitment (KnowledgePanel provides internet access for those who do not have it and, if needed, a device to access the internet when they join the panel). A combination of random-digit dialing (RDD) and address-based sampling (ABS) methodologies have been used to recruit panel members (in 2009 KnowledgePanel switched its sampling methodology for recruiting panel members from RDD to ABS). The panel includes households with landlines and cellular phones, including those only with cellphones, and those without a phone. Both the RDD and ABS samples were provided by Marketing Systems Group.
KnowledgePanel continually recruits new panel members throughout the year to offset panel attrition as people leave the panel. All active adult members of the Ipsos panel were eligible for inclusion in this study. In all, 5,797 panelists were invited to take part in the survey, for a study completion rate of 61.2%. All sampled members received an initial email to notify them of the survey and provide a link to the survey questionnaire. Additional follow-up reminders were sent to those who had not yet responded as needed.
The cumulative response rate accounting for nonresponse to the recruitment surveys and attrition is 4.0%. The break-off rate among panelists who logged onto the survey and completed at least one item is 5.4%.
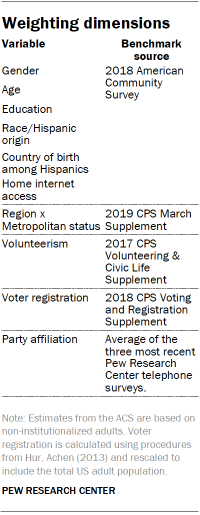
The data were weighted in a multistep process that begins with a base weight incorporating the respondents’ original selection probability. The next step in the weighting uses an iterative technique that aligns the sample to population benchmarks on the dimensions listed in the accompanying table.
Sampling errors and test of statistical significance take into account the effect of weighting. Interviews are conducted in both English and Spanish.
In addition to sampling error, one should bear in mind that question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of opinion polls.
The following table shows the unweighted sample sizes and the error attributable to sampling that would be expected at the 95% level of confidence for different groups in the survey:
Sample sizes and sampling errors for other subgroups are available upon request.
Coding of open-ended origin responses
Origins provided in the write-in boxes for those who selected White, Black or “some other race” were coded into five geographic regions according to the country they corresponded with, under the following framework. Mentions of “African American” were coded separately. Up to two mentions of a geographic region were coded, so the totals may add to greater than 100%.
Americas
American
Anguilla
Antigua and Barbuda
Aruba
Bahamas
Barbados
British Virgin Islands
Caribbean Netherlands
Cayman Islands
Cuba
Curacao
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Haiti
Jamaica
Martinique
Montserrat
Puerto Rico
Sint Maarten
St. Barthelemy
St. Kitts and Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
Trinidad and Tobago
Turks and Caicos Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Belize
Costa Rica
El Salvador
Guatemala
Hispanic
Honduras
Latino
Mexico
Nicaragua
Panama
Argentina
Bolivia
Brazil
Chile
Colombia
Ecuador
Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
French Guiana
Guyana
Paraguay
Peru
Suriname
Uruguay
Venezuela
Bermuda
Canada
Greenland
St. Pierre and Miquelon
United States
Asia
Azerbaijan
Kazakhstan
Kyrgyzstan
Tajikistan
Turkmenistan
Uzbekistan
Brunei
Burma (Myanmar)
Cambodia
China
Hong Kong
Indonesia
Japan
Laos
Macao
Malaysia
Mongolia
North Korea
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Singapore
South Korea
Taiwan
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Vietnam
American Samoa
Australia
Cook Islands
Federated States of Micronesia
Fiji
French Polynesia
Guam
Kiribati
Marshall Islands
Nauru
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Niue
Northern Mariana Islands
Palau
Samoa
Solomon Islands
Tokelau
Tonga
Tuvalu
Vanuatu
Wallis and Futuna
Afghanistan
Bangladesh
Bhutan
India
Maldives
Nepal
Pakistan
Sri Lanka
Europe
Albania
Armenia
Belarus
Bosnia-Herzegovina
Bulgaria
Caucasian
Croatia
Czech Republic
Estonia
Georgia
Hungary
Kosovo
Latvia
Lithuania
Moldova
Montenegro
North Macedonia
Poland
Romania
Russia
Serbia
Slovakia
Slovenia
Ukraine
Andorra
Austria
Belgium
Channel Islands
Cyprus
Denmark
Faeroe Islands
Finland
France
Germany
Gibraltar
Greece
Iceland
Ireland
Isle of Man
Italy
Liechtenstein
Luxembourg
Malta
Monaco
Netherlands
Norway
Portugal
San Marino
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
United Kingdom
Vatican City
Middle East-North Africa
Algeria
Libya
Morocco
Sudan
Tunisia
Western Sahara
Bahrain
Egypt
Iran
Iraq
Israel
Jordan
Kuwait
Lebanon
Oman
Palestinian territories
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
Syria
Turkey
United Arab Emirates
Yemen
Sub-Saharan Africa
Angola
Benin
Botswana
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cameroon
Cape Verde
Central African Republic
Chad
Comoros
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Djibouti
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Ethiopia
Gabon
Gambia
Ghana
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Ivory Coast
Kenya
Lesotho
Liberia
Madagascar
Malawi
Mali
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mozambique
Namibia
Niger
Nigeria
Republic of the Congo
Reunion
Rwanda
Sao Tome and Principe
Senegal
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Swaziland
Tanzania
Togo
Uganda
Zambia
Zimbabwe