This report is drawn from a survey conducted as part of the American Trends Panel (ATP), a nationally representative panel of randomly selected U.S. adults living in households recruited from landline and cellphone random-digit-dial (RDD) surveys. Panelists participate via monthly self-administered web surveys. Panelists who do not have internet access are provided with a tablet and wireless internet connection. The panel was created by Pew Research Center is being managed by GfK.
Data in this report are drawn from the panel wave conducted March 27-April 9, 2018, among 2,541 respondents. The margin of sampling error for the full sample of 2,541 respondents is plus or minus 2.7 percentage points.
Members of the ATP were recruited from several large, national landline and cellphone RDD surveys conducted in English and Spanish. At the end of each survey, respondents were invited to join the panel. The first group of panelists was recruited from the 2014 Political Polarization and Typology Survey, conducted Jan. 23 to March 16, 2014. Of the 10,013 adults interviewed, 9,809 were invited to take part in the panel and a total of 5,338 agreed to participate.5 The second group of panelists was recruited from the 2015 Pew Research Center Survey on Government, conducted Aug. 27 to Oct. 4, 2015. Of the 6,004 adults interviewed, all were invited to join the panel, and 2,976 agreed to participate.6 The third group of panelists was recruited from a survey conducted April 25 to June 4, 2017. Of the 5,012 adults interviewed in the survey or pretest, 3,905 were invited to take part in the panel and a total of 1,628 agreed to participate.7
The overall target population for Wave 33 was non-institutionalized persons age 18 and over, living in the United States, including Alaska and Hawaii. The sample consisted of 3,102 ATP members. This subsample was selected using the following approach:
- Panelists were grouped into three strata based on how underrepresented they are demographically. Then we analyzed response rates to the last five panel survey waves (W28-32) to project the number of panelists in each stratum who would respond to the W33 survey.
- We then determined how many panelists we wanted to sample from each stratum in W33 in order to finish with around 2,500 completed interviews and have a responding sample that is as representative as possible.
- Stratum A consists of panelists who are non-internet users, black non-Hispanic, Hispanic, or high school or less education. There were 1,819 total panelists in this stratum and they are sampled at a rate of 100% for W33. 1,806 were active panelists.
- Stratum B consists of panelists that are ages 18 to 34 or are non-volunteers. The 1,684 total panelists in this stratum are subsampled at a rate of 63%, yielding 1,061 sampled for W33 (1,057 were active).
- Stratum C consists of the remaining 2,009 panelists not in stratum A or B. This group is subsampled at a rate of 12%, yielding 241 panelists sampled for W33 (239 were active).
The ATP data were weighted in a multi-step process that begins with a base weight incorporating the respondents’ original survey selection probability and the fact that in 2014 some panelists were subsampled for invitation to the panel. Next, an adjustment was made for the fact that the propensity to join the panel and remain an active panelist varied across different groups in the sample. The final step in the weighting uses an iterative technique that aligns the sample to population benchmarks on a number of dimensions. Gender, age, education, race, Hispanic origin and region parameters come from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2016 American Community Survey. The county-level population density parameter (deciles) comes from the 2010 U.S. decennial census. The telephone service benchmark comes from the July-December 2016 National Health Interview Survey and is projected to 2017. The volunteerism benchmark comes from the 2015 Current Population Survey Volunteer Supplement. The party affiliation benchmark is the average of the three most recent Pew Research Center general public telephone surveys. The internet access benchmark comes from the 2017 ATP Panel Refresh Survey. Respondents who did not previously have internet access are treated as not having internet access for weighting purposes. Sampling errors and statistical tests of significance take into account the effect of weighting. Interviews are conducted in both English and Spanish, but the Hispanic sample in the ATP is predominantly U.S. born and English speaking.
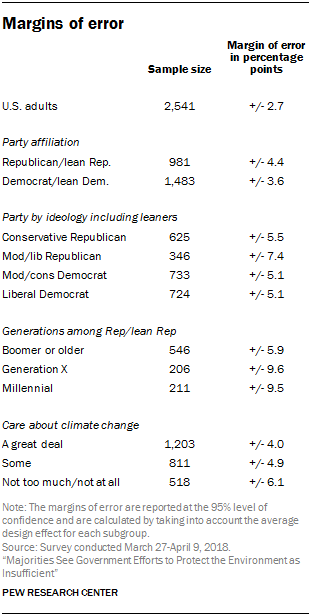
Margins of error tables shown here provide the unweighted sample sizes and the error attributable to sampling that would be expected at the 95% level of confidence for different groups in the survey taking into account the average design effect for each subgroup. Sample sizes and sampling errors for other subgroups are available upon request.
In addition to sampling error, one should bear in mind that question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of opinion polls.
The March 2018 wave had a response rate of 82 % (2,541 responses among 3,102 individuals in the panel). Taking account of the combined, weighted response rate for the recruitment surveys (10.0%) and attrition from panel members who were removed at their request or for inactivity, the cumulative response rate for the wave is 2.3%8.
© Pew Research Center, 2018




